The Dental Admission Test (DAT) is a comprehensive assessment developed by the American Dental Association (ADA) to evaluate the readiness and potential of candidates for dental school.
Purpose: The primary purpose of the DAT is to provide dental education programs with a reliable measure of applicants’ academic abilities and critical thinking skills necessary for success in the demanding field of dentistry.
Skills Measured: The DAT assesses a broad range of skills across four main sections: Survey of the Natural Sciences, Perceptual Ability, Reading Comprehension, and Quantitative Reasoning. The Survey of the Natural Sciences covers biology, general chemistry, and organic chemistry. The Perceptual Ability Test (PAT) measures spatial visualization skills, essential for interpreting two-dimensional representations of three-dimensional objects. The Reading Comprehension section tests the ability to understand and analyze scientific passages. The Quantitative Reasoning section assesses mathematical problem-solving abilities.
Format: The DAT is a computer-based test consisting of 280 multiple-choice questions, administered over 5 hours and 15 minutes. The test includes an optional 30-minute break, helping candidates manage the rigorous examination schedule effectively.
Validity: The validity of the DAT as an assessment tool is well-established. Studies conducted by the ADA’s Department of Testing Services (DTS) demonstrate that DAT scores, when combined with academic performance, are strong predictors of success in dental education programs. The exam undergoes rigorous development and annual reviews by subject matter experts to ensure its content remains current and accurately reflects the knowledge and skills required in modern dentistry.
For aspiring dental students, the DAT is not merely an entry requirement but a critical step in demonstrating their aptitude and commitment to the field.
Did you know?
Did you know that the DAT’s Perceptual Ability Test is considered one of the most challenging sections, requiring intense spatial visualization skills? Scoring is scaled from 1 to 30, with no penalties for guessing. Successful test takers often have a background in rigorous science courses and superb time management skills. Administered via Prometric centers, DAT results not only influence dental school admissions but also hint at future performance, catching the eye of potential employers.
DAT Navigation Pad
Question Types Explained
The DAT comprises four main sections, each designed to test different skills essential for success in dental school. The table below provides an overview of the sections, the number of questions, the topics covered, and the key skills needed to perform well.
| Section | #Questions/ Minutes | Topics Covered | Skills Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survey of the Natural Sciences | 100/90 | Biology (40): Cell & Molecular Biology, Diversity of Life, Systems, Genetics, Evolution, Ecology General Chemistry (30): Stoichiometry, Gases, Liquids, Solids, Solutions, Acids & Bases, Equilibria, Thermodynamics, Kinetics, Redox, Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties, Nuclear Reactions, Lab Techniques Organic Chemistry (30): Mechanisms, Properties, Stereochemistry, Nomenclature, Functional Groups, Acid-Base, Aromatics, Bonding | In-depth knowledge of biological, chemical, and organic chemistry concepts; problem-solving; laboratory skills |
| Perceptual Ability Test (PAT) | 90/60 | Apertures, View Recognition, Angle Discrimination, Paper Folding, Cube Counting, 3D Form Development | Spatial visualization, problem-solving, attention to detail |
| Reading Comprehension Test | 50/60 | Scientific passages | Reading comprehension, analytical thinking, synthesis of information |
| Quantitative Reasoning Test | 40/45 | Algebra, Equations, Inequalities, Exponentials, Ratios, Proportions, Graphical Analysis, Data Interpretation, Quantitative Comparison, Probability, Statistics | Mathematical skills, data analysis, problem-solving |
The DAT evaluates candidates across various sections, each focusing on specific skills crucial for dental education and practice. Understanding the structure and content of these sections is vital for effective preparation and success in the test.
Here’s a detailed overview of each section and the necessary skills to perform well:
1. Survey of the Natural Sciences
This section includes 100 questions divided into three subsections: Biology, General Chemistry, and Organic Chemistry.
Biology (40 questions):
- Topics: Cell and Molecular Biology, Diversity of Life, Structure and Function of Systems, Genetics, Evolution, and Ecology.
- Skills Needed: Strong foundational knowledge in biological concepts, the ability to understand complex processes, and recall detailed information.
General Chemistry (30 questions):
- Topics: Stoichiometry, Gases, Liquids and Solids, Solutions, Acids and Bases, Chemical Equilibria, Thermodynamics, Chemical Kinetics, Oxidation-Reduction Reactions, Atomic and Molecular Structure, Periodic Properties, Nuclear Reactions, and Laboratory Techniques.
- Skills Needed: Proficiency in chemical calculations, understanding of chemical principles, and familiarity with laboratory practices.
Organic Chemistry (30 questions):
- Topics: Reaction Mechanisms, Chemical Properties of Molecules, Stereochemistry, Nomenclature, Reactions of Major Functional Groups, Acid-Base Chemistry, Aromatics and Bonding.
- Skills Needed: Knowledge of organic reactions, ability to predict reaction outcomes, and comprehension of molecular structures and properties .
2. Perceptual Ability Test (PAT)
This section comprises 90 questions divided into six subtests, assessing spatial visualization and problem-solving skills.
Subtests:
- Apertures: Determining if objects can pass through openings.
- View Recognition: Visualizing objects from different angles.
- Angle Discrimination: Ranking angles from smallest to largest.
- Paper Folding: Unfolding a punched and folded paper.
- Cube Counting: Evaluating exposed sides of stacked cubes.
- 3D Form Development: Identifying 3D shapes formed from flat patterns.
Skills Needed: Strong spatial reasoning, ability to visualize and manipulate objects in space, and acute attention to detail .
3. Reading Comprehension Test
This section includes 50 questions based on three reading passages related to scientific topics.
Skills Needed: Ability to quickly read and understand scientific passages, analyze and synthesize information, and draw logical conclusions based on the text.
4. Quantitative Reasoning Test
This section consists of 40 questions that assess mathematical problem-solving abilities.
Topics:
- Mathematical Problems: Algebra, equations, inequalities, exponentials, ratios, proportions, graphical analysis.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: Interpretation of data and sufficiency.
- Quantitative Comparison: Comparing quantities to determine relationships.
- Probability and Statistics: Basic probability and statistical analysis.
Skills Needed: Strong mathematical skills, proficiency in algebra and geometry, and ability to analyze and interpret data accurately .
Mastering these sections requires dedicated preparation, strong foundational knowledge in sciences, excellent spatial reasoning, and proficient mathematical skills.
“The DAT was definitely challenging, especially the Perceptual Ability Test. I found the spatial reasoning questions to be quite tough, but with practice, I got the hang of it. The Natural Sciences section was extensive, covering a lot of detailed concepts in biology and chemistry. The Reading Comprehension passages were longer than I expected, so time management was crucial. Overall, the test really pushed me to apply my knowledge practically.”
— Jonathan Rivera, Dental Student. Source: Reddit
Preparation Strategies
Preparing for the DAT requires a strategic approach, combining thorough review of content areas with practice and time management. Here is a comprehensive guide to help you succeed:
1. Understand the Test Format and Content
- Familiarize yourself with the structure and timing of the DAT. The test includes sections on Natural Sciences, Perceptual Ability, Reading Comprehension, and Quantitative Reasoning.
- Review the official DAT Candidate Guide for detailed information on the topics covered in each section .
2. Create a Study Schedule
- Develop a study plan that covers all sections of the DAT, allocating more time to areas where you are less confident.
- Break down your study sessions into manageable chunks, focusing on one topic at a time to avoid burnout.
3. Take Practice Tests
- Regularly take full-length practice tests under timed conditions to build stamina and get accustomed to the test’s pacing.
- Analyze your practice test results to identify weaknesses and adjust your study plan accordingly.
4. Review Key Concepts
- For the Natural Sciences section, focus on biology, general chemistry, and organic chemistry. Ensure you understand fundamental concepts and can apply them to different scenarios.
- Practice spatial reasoning skills for the Perceptual Ability Test (PAT) by using PAT-specific practice materials.
5. Enhance Reading and Analytical Skills
- Improve your reading comprehension by reading scientific articles and practicing summarizing key points.
- Work on interpreting data and solving complex problems for the Quantitative Reasoning section.
6. Join Study Groups
- Collaborate with peers to discuss challenging concepts and quiz each other. Group study can provide different perspectives and enhance your understanding.
7. Stay Consistent
- Maintain a consistent study routine. Avoid cramming, as it is less effective than steady, incremental learning.
8. Take Care of Yourself
- Ensure you get enough sleep, eat healthily, and take regular breaks during your study sessions. Physical and mental well-being significantly impact your performance.
9 Simulate Test Day
- Use Prometric’s Test Drive to become familiar with the testing environment and procedures. This experience includes a 30-minute overview of what to expect on test day .
By following these preparation strategies, you can approach the DAT with confidence and increase your chances of achieving a high score.
“Taking the DAT was a rigorous experience. The Quantitative Reasoning section required sharp problem-solving skills and quick thinking. I appreciated the structured format, but staying focused for over five hours was demanding. The survey of natural sciences was comprehensive, testing everything from cell biology to organic chemistry. I’d advise future test-takers to be thorough with their foundational knowledge.”
— Erica White, Pre-Dental Advisor. Source: reddit
Test Features
The Dental Admission Test (DAT) is a comprehensive and standardized examination designed to assess the academic and perceptual abilities of prospective dental students. Here are the main features of the DAT:
Purpose:
- The DAT is intended to evaluate a candidate’s readiness and potential for success in dental school. It is a critical component of the dental school admission process in the United States and Canada.
Content:
- The test comprises four sections: Survey of the Natural Sciences, Perceptual Ability, Reading Comprehension, and Quantitative Reasoning. Each section targets specific skills and knowledge areas essential for dental education.
Test Format:
- The DAT is a computer-based test administered at Prometric test centers. It includes 280 multiple-choice questions and spans a total time of 5 hours and 15 minutes, which includes an optional 30-minute break.
Scoring:
- Scores range from 1 to 30 for each section. The scoring process uses sophisticated psychometric techniques to ensure fairness and accuracy, allowing comparison across different test versions.
Test Development and Fairness:
- The test questions are developed and reviewed by a team of subject matter experts and are updated annually to reflect current scientific knowledge and practices. The DAT adheres to strict guidelines to ensure fairness, validity, and reliability.
Adaptive Testing:
- While the DAT is not adaptive in the traditional sense, it includes unscored experimental questions that are indistinguishable from scored questions. These are used to gather data for future test versions.
Administration:
- Candidates must register and schedule their test through the Prometric website. The administration process includes biometric verification to ensure test security and integrity.
Usage of Results:
- Dental schools use DAT scores as one of the multiple criteria for evaluating applicants. The scores provide insight into a candidate’s academic strengths and weaknesses, helping admissions committees make informed decisions.
Common names for the DAT Test
- Dental Admission Test (DAT)
- ADA DAT
- Dental Aptitude Test
- Dental School Entrance Exam
“What worked best for me was taking multiple practice tests under timed conditions. This helped me manage my time effectively and get used to the test format. I also joined a study group where we quizzed each other on tough concepts. It made a huge difference in my understanding and retention.”
— David Kim, Dental Assistant. Source: reddit
Technical Facts
The Dental Admission Test (DAT) includes various technical details essential for candidates to understand before taking the exam. Here are key technical facts about the DAT:
Length and Timing:
- Total test time: 5 hours and 15 minutes, including an optional 30-minute break.
- Breakdown: Survey of the Natural Sciences (90 minutes), Perceptual Ability Test (60 minutes), Reading Comprehension Test (60 minutes), Quantitative Reasoning Test (45 minutes).
Question Format:
- The exam consists of 280 multiple-choice questions.
- Questions are distributed as follows: 100 questions for the Survey of the Natural Sciences, 90 for the Perceptual Ability Test, 50 for the Reading Comprehension Test, and 40 for the Quantitative Reasoning Test.
Administration:
- Administered at Prometric test centers.
- Candidates must present valid identification and undergo biometric verification.
Scoring:
- Scores range from 1 to 30 for each section.
- No penalties for guessing; only correct answers are counted.
- Some questions are unscored and used for future test development.
Test Environment:
- Secure testing area with strict rules prohibiting personal items.
- Test centers provide note boards and low-odor markers for rough work.
Eligibility and Registration:
- Typically, candidates should have completed at least one year of college education.
- Registration is completed through the ADA website, and testing appointments are scheduled via Prometric.
Confidentiality:
- Examination content is confidential and copyrighted. Sharing or discussing test items is strictly prohibited.
Fairness and Validity:
- The test is designed to be fair and valid, with annual reviews by subject matter experts to ensure the content reflects current scientific knowledge.
- The ADA adheres to professional standards for educational and psychological testing to maintain test fairness and reliability.
Test Fees and Costs
This table outlines the various fees associated with taking the DAT, including additional services and retake policies.
| Fee Type | Description | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Examination Fee | Includes administration and score reporting to selected schools | $540 |
| Score Report Fee (optional) | For additional score reports requested after the initial application | $50 per report |
| Score Audit Fee (optional) | For requesting an audit of your scores within 30 days of the test date | $65 |
| Eligibility Extension Fee | For extending the eligibility period by 45 days | $135 |
| Rescheduling Fee (30+ days) | Rescheduling test date 30 or more business days before the test | $40 |
| Rescheduling Fee (5-29 days) | Rescheduling test date 5-29 business days before the test | $70 |
| Rescheduling Fee (1-4 days) | Rescheduling test date 1-4 business days before the test | $150 |
“The Reading Comprehension section was unexpectedly tricky. The passages were dense and required careful analysis. The Perceptual Ability Test had some of the most unique questions I’ve ever encountered, like angle discrimination and paper folding. The experience was intense but also rewarding because it tested a broad range of skills essential for dentistry.”
— Michael Thompson, Dental Hygienist. Source: Reddit
Results Scale and Interpretations
The Dental Admission Test (DAT) employs a sophisticated scoring system designed to provide an accurate and fair evaluation of a candidate’s abilities. Understanding how the scores are calculated and interpreted can help you assess your performance and plan your next steps.
Raw Score vs. Scale Score
- Raw Score: This is the total number of correct answers. There are no penalties for guessing, so it’s beneficial to answer every question.
- Scale Score: The raw scores are converted into scale scores ranging from 1 to 30. This conversion accounts for any differences in difficulty across different test forms to ensure fairness.
Percentile Ranking
- Percentile Ranking: This indicates how your performance compares to that of other test-takers. For example, if your percentile rank is 75, it means you scored higher than 75% of the candidates.
Sub-scores
- Each section of the DAT (Survey of the Natural Sciences, Perceptual Ability, Reading Comprehension, and Quantitative Reasoning) receives its own scale score, providing a detailed insight into your strengths and weaknesses.
Score Range
- Score Range: The scale scores for each section range from 1 to 30. While there is no official passing score, most dental schools consider scores above 20 to be competitive.
Score Report Components
- Academic Average (AA): An average of the scale scores from the Survey of the Natural Sciences, Reading Comprehension, and Quantitative Reasoning sections.
- Total Science (TS): A combined score reflecting your performance in biology, general chemistry, and organic chemistry.
- Perceptual Ability Test (PAT): A separate score evaluating your spatial and perceptual abilities.
Example Score Ranges and Interpretations
- 21-30: Excellent – Reflects a strong understanding and high proficiency in the tested areas. Competitive for most dental programs.
- 18-20: Good – Demonstrates solid knowledge and skills. Likely competitive for many programs.
- 15-17: Average – Indicates adequate performance but may require improvement for more competitive programs.
- Below 15: Below Average – Suggests the need for significant improvement in preparation.
How to Use Your Score Report
- Self-Assessment: Identify areas of strength and weakness. Focus your preparation on weaker areas for improvement.
- Advising: Discuss your scores with an academic advisor to determine the best course of action, whether it’s retaking the test or applying to specific programs.
- Application Enhancement: Use your scores to highlight your strengths in applications, and complement them with other strong credentials like GPA and extracurricular activities.
Understanding your DAT scores helps you better prepare for your future in dental education and ensures you are well-equipped to meet the expectations of your desired programs. By interpreting your results accurately, you can make informed decisions about your next steps in the admission process.

iPREP: Concise. Focused. What you need.
Sign up
Immediate access
Practice
Online self-paced
Pass
Ace that Test!
FAQs
The Dental Admission Test (DAT) is a standardized examination designed to assess the academic abilities and perceptual skills of candidates seeking admission to dental schools in the United States and Canada.
The DAT evaluates a range of skills including knowledge in natural sciences (biology, general chemistry, organic chemistry), perceptual ability, reading comprehension, and quantitative reasoning.
The DAT is composed of four sections: Survey of the Natural Sciences, Perceptual Ability Test (PAT), Reading Comprehension Test, and Quantitative Reasoning Test. The test includes 280 multiple-choice questions and is administered over 5 hours and 15 minutes.
Scores for each section range from 1 to 30. The raw score (number of correct answers) is converted to a scaled score to account for differences in test difficulty. The score report also includes a percentile ranking, academic average, and total science score.
A score of 21-30 is considered excellent and highly competitive. Scores of 18-20 are good and competitive for many programs, while scores below 15 may require significant improvement.
Effective preparation strategies include understanding the test format, creating a study schedule, using official study materials, taking practice tests, reviewing key concepts, joining study groups, and taking care of your physical and mental health.
Yes, candidates can retake the DAT, but there are restrictions on the number of retakes and the interval between attempts. It is important to check the specific retake policies and plan accordingly.
Dental schools use DAT scores as a critical component of their admission process to assess an applicant’s readiness and potential for success. Scores are considered alongside other factors such as GPA, letters of recommendation, and personal statements.
Primarily, the DAT is used for dental school admissions. However, high DAT scores can also be an indicator of strong academic abilities and may be noted by employers during job applications or by educational programs for scholarships and honors.
On test day, you should expect to undergo biometric verification, adhere to strict security protocols, and be provided with necessary testing materials such as note boards and markers. It is essential to bring valid identification and follow all test center procedures.
“Flashcards were my go-to for memorizing biology and chemistry terms. I also watched online tutorials for organic chemistry reactions, which made the content more digestible. Taking a ‘test drive’ at the Prometric center helped ease my nerves on test day because I knew exactly what to expect.”
— Priya Kumar, Dental Technician. Source: Reddit
Test Tips
- Arrive Early: Arriving at least 30 minutes before your scheduled test time allows you to complete the check-in process without stress. Rushing to the test center can increase anxiety and affect your performance. Remember, punctuality is key to a calm start.
- Dress Comfortably: Wear comfortable clothing to ensure you’re physically at ease during the test. The testing center environment can be unpredictable, so dress in layers to adjust to varying temperatures.
- Manage Your Time Wisely: Keep an eye on the clock and pace yourself. Allocate specific time blocks for each section and stick to them. Don’t spend too much time on any single question; if you’re stuck, move on and return to it if time permits.
- Utilize the Optional Break: Take advantage of the optional 30-minute break after the first two sections. Use this time to stretch, hydrate, and clear your mind. Avoid discussing test content or checking study materials during this break to maintain focus.
- Stay Calm and Focused: It’s normal to feel nervous, but staying calm is crucial. Practice deep breathing techniques to manage anxiety. If you find yourself panicking, take a moment to breathe deeply and refocus on the task at hand.
- Use the Note Boards Effectively: Use the provided note boards for rough work, especially for the Quantitative Reasoning section. Jot down key points and calculations to avoid confusion. Remember, these boards are there to help you organize your thoughts and answers.
- Double-Check Your Answers: If time allows, review your answers, especially for sections where accuracy is critical, like the Survey of the Natural Sciences. Ensure you haven’t left any questions unanswered and that your responses are recorded correctly.
Following these tips will help you navigate the test day smoothly and maximize your performance on the DAT. Stay confident, manage your time, and trust in your preparation.
Administration
- Test Location: The DAT is administered at Prometric test centers, which are located throughout the United States and Canada.
- Test Schedule: Candidates can schedule their test year-round, depending on the availability of test centers. It is recommended to book early to secure your preferred date and time.
- Test Format: The DAT is a computerized test consisting of multiple-choice questions. There are no open-ended questions.
- Test Materials: Personal items, including pens and paper, are not allowed in the testing room. Test centers provide note boards and low-odor markers for rough work. All necessary materials will be supplied by the test center.
- Cost: The fee for the DAT is $540, which includes the administration of the test and official score reporting to the schools selected at the time of application.
- Retake Policy: Candidates must wait 60 days between testing attempts. You can retake the DAT up to three times without special permission. For more than three attempts, you must apply for permission to test again and provide evidence of your application to dental schools.
Test Provider
The Dental Admission Test (DAT) is administered by the American Dental Association (ADA), a professional organization established in 1859. The ADA aims to advance the dental profession on a global scale through research, advocacy, and the development of high standards in dental education and practice. With over 163,000 members, the ADA is dedicated to improving oral health and promoting the art and science of dentistry.
The ADA offers a range of services, including the development and administration of standardized tests like the DAT, which assess the competencies required for dental education and licensure. Globally, the ADA is known for its top products such as the ADA Seal of Acceptance for dental products, continuing education programs, and the Journal of the American Dental Association (JADA), which disseminates cutting-edge research and clinical practices in dentistry.
Information Sources
- American Dental Association (ADA) – DAT
- Prometric – Test Centers
- ADA.org – DAT Candidate Guide
- Dental Admission Testing Program – DAT
- ADA.org – Dental Personal Identifier Number (DENTPIN)
Disclaimer – All the information and prep materials on iPREP are genuine and were created for tutoring purposes. iPREP is not affiliated with the American Dental Association (ADA), which is the owner of the DAT Test, or with any of the companies or organizations mentioned above.
Free DAT practice test: Get to know what the DAT Test will be like by practicing with these sample questions:
1. Survey of the Natural Sciences (SNS)
SNS Question 1 of 6
Which of the following processes occurs in the mitochondria?
- Photosynthesis
- Glycolysis
- Calvin cycle
- Krebs cycle
- Transcription
Answer: D. Krebs cycle
Explanation:
- A. Photosynthesis: Incorrect. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
- B. Glycolysis: Incorrect. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- C. Calvin cycle: Incorrect. The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
- D. Krebs cycle: Correct. The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, occurs in the mitochondria.
- E. Transcription: Incorrect. Transcription occurs in the nucleus where DNA is transcribed to mRNA.
SNS Question 2 of 6
What is the main function of ribosomes in a cell?
- Lipid synthesis
- Protein synthesis
- DNA replication
- Cell division
- Photosynthesis
Answer: B. Protein synthesis
Explanation:
- A. Lipid synthesis: Incorrect. Lipid synthesis occurs in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
- B. Protein synthesis: Correct. Ribosomes are responsible for synthesizing proteins by translating mRNA.
- C. DNA replication: Incorrect. DNA replication occurs in the nucleus during the S phase of the cell cycle.
- D. Cell division: Incorrect. Cell division is a process involving various structures, but not ribosomes specifically.
- E. Photosynthesis: Incorrect. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
SNS Question 3 of 6
Which gas law is represented by the equation PV=nRT?
- Boyle’s Law
- Charles’s Law
- Avogadro’s Law
- Ideal Gas Law
- Dalton’s Law
Answer: D. Ideal Gas Law
Explanation:
- A. Boyle’s Law: Incorrect. Boyle’s Law states that pressure and volume are inversely proportional at constant temperature.
- B. Charles’s Law: Incorrect. Charles’s Law states that volume is directly proportional to temperature at constant pressure.
- C. Avogadro’s Law: Incorrect. Avogadro’s Law states that volume is directly proportional to the number of moles at constant temperature and pressure.
- D. Ideal Gas Law: Correct. The Ideal Gas Law is represented by the equation PV=nRTPV = nRTPV=nRT, relating pressure, volume, number of moles, gas constant, and temperature.
- E. Dalton’s Law: Incorrect. Dalton’s Law pertains to partial pressures in a gas mixture.
SNS Question 4 of 6
Which phase of mitosis is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes along the metaphase plate?
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
- Cytokinesis
Answer: B. Metaphase
Explanation:
- A. Prophase: Incorrect. During prophase, chromosomes condense and become visible, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- B. Metaphase: Correct. Metaphase is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes along the metaphase plate (equatorial plane).
- C. Anaphase: Incorrect. During anaphase, sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles.
- D. Telophase: Incorrect. Telophase involves the reformation of the nuclear envelope around the separated chromatids.
- E. Cytokinesis: Incorrect. Cytokinesis is the process of cytoplasmic division, completing cell division.
SNS Question 5 of 6
Which molecule is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain of cellular respiration?
- NADH
- FADH2
- Oxygen (O2)
- Water (H2O)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Answer: C. Oxygen (O2)
Explanation:
- A. NADH: Incorrect. NADH is an electron donor in the electron transport chain.
- B. FADH2: Incorrect. FADH2 is also an electron donor in the electron transport chain.
- C. Oxygen (O2): Correct. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, forming water.
- D. Water (H2O): Incorrect. Water is a product formed when oxygen accepts electrons.
- E. Carbon dioxide (CO2): Incorrect. Carbon dioxide is a byproduct of the Krebs cycle and is not involved in the electron transport chain.
SNS Question 6 of 6
Which of the following best describes the function of the Golgi apparatus?
- DNA replication
- ATP production
- Protein modification and sorting
- Lipid synthesis
- Photosynthesis
Answer: C. Protein modification and sorting
Explanation:
- A. DNA replication: Incorrect. DNA replication occurs in the nucleus.
- B. ATP production: Incorrect. ATP production occurs in the mitochondria through cellular respiration.
- C. Protein modification and sorting: Correct. The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or use within the cell.
- D. Lipid synthesis: Incorrect. Lipid synthesis primarily occurs in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
- E. Photosynthesis: Incorrect. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
2. Perceptual Ability Test (PAT)
In this 2D 3D sample exercise, your goal is to find the pairs that match up.
2D-3D Question 1 of 2
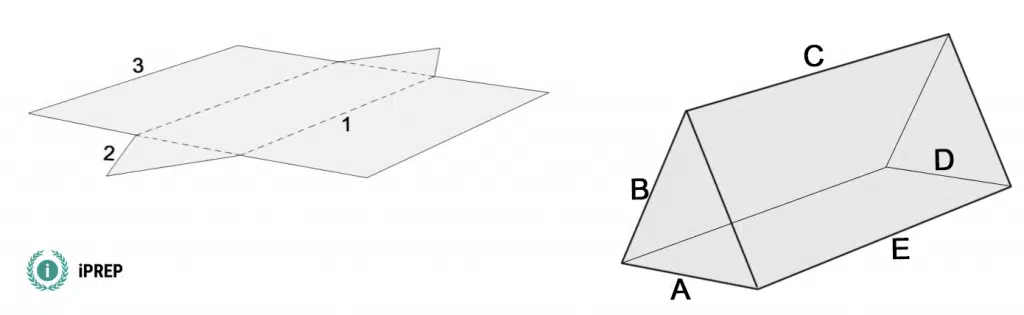
Select the pairs that correspond:
- 1-E & 3-C
- 1-C & 2-B
- 2-A & 3-D
- 3-D & 2-B
- 1-C & 3-A
The pairs 1-E and 3-C correctly correspond. Please find an animated illustration below.
2D-3D Question 2 of 2
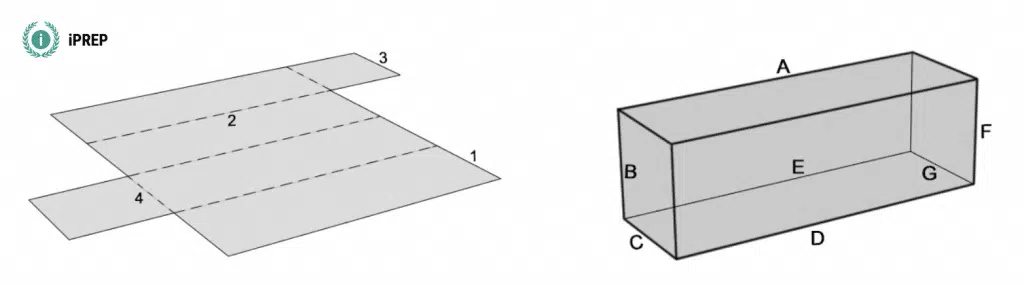
Select the pairs that correspond:
- 1-A & 4-C
- 3-F & 2-B
- 1-C & 2-G
- 4-C & 3-G
- 2-E & 4-A
The pairs 4-C and 3-G correctly correspond. Please find an animated illustration below.
Paper Folding Sample Question
Paper Folding Test Instructions
This test is designed to assess your ability to understand and visualize three-dimensional objects. Each question presents a sequence of images. On the left-hand side you will see a series of images depicting the folding process of a square sheet of paper. The final image in this series will display the paper after one or two holes have been punched through it, following its folding. On the right-hand side, you will encounter images of five unfolded papers. Your task is to identify which among these five images accurately represents the paper’s appearance with the holes once it is fully unfolded. Select the correct image and mark its corresponding letter.
Please review the example problem provided below to familiarize yourself with this test.
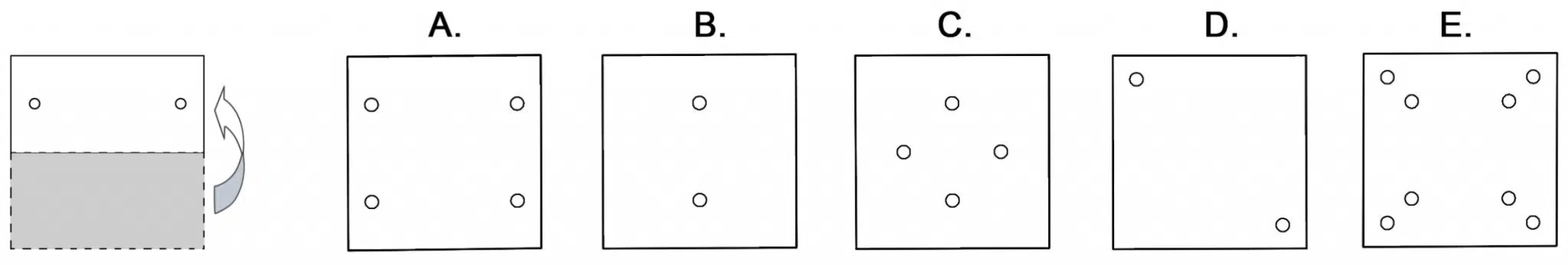
The correct answer is A.
Watch the video below for the solution explanation:
3. Reading Comprehension Test
Reading Passage: The Importance of Biofilms in Dentistry
Biofilms are complex communities of microorganisms that attach to surfaces in the oral cavity, including teeth, gums, and dental prosthetics. These microbial communities are embedded in a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), which provide structural integrity and protection to the bacteria within the biofilm. Biofilms play a significant role in dental health, contributing to both beneficial and pathogenic processes.
One of the primary benefits of biofilms is their ability to protect the host from pathogenic microorganisms by outcompeting them for resources and space. The normal oral microbiota forms a protective barrier that inhibits the colonization of harmful pathogens. However, when the balance of these microbial communities is disrupted, pathogenic biofilms can form, leading to dental diseases such as caries and periodontitis.
Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay, is primarily caused by acidogenic bacteria within the biofilm that metabolize dietary sugars and produce acids. These acids demineralize the enamel and dentin, leading to cavity formation. Streptococcus mutans is one of the most well-known acidogenic bacteria involved in this process. Periodontitis, on the other hand, is an inflammatory disease affecting the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums and bone. It is caused by pathogenic biofilms that elicit an immune response, leading to tissue destruction.
Managing biofilms in dentistry involves both preventive and therapeutic approaches. Regular oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing, disrupt biofilm formation and reduce the risk of dental diseases. Professional dental cleanings and the use of antimicrobial agents can also help control biofilm-associated infections. Understanding the dynamics of biofilm formation and maintenance is crucial for developing effective dental treatments and promoting oral health.
Reading Comprehension Question 1 of 6
What is the primary function of the extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in biofilms?
- To metabolize dietary sugars
- To provide structural integrity and protection to the bacteria
- To produce acids that demineralize enamel
- To elicit an immune response
- To disrupt biofilm formation
Answer: B. To provide structural integrity and protection to the bacteria
Explanation:
- A. To metabolize dietary sugars: Incorrect. Metabolizing dietary sugars is the function of acidogenic bacteria within the biofilm, not the EPS.
- B. To provide structural integrity and protection to the bacteria: Correct. The EPS matrix provides structural integrity and protection to the bacteria within the biofilm.
- C. To produce acids that demineralize enamel: Incorrect. Acid production is a function of certain bacteria like Streptococcus mutans, not the EPS.
- D. To elicit an immune response: Incorrect. Pathogenic biofilms can elicit an immune response, but this is not the function of the EPS.
- E. To disrupt biofilm formation: Incorrect. EPS actually supports biofilm formation by providing structure and protection.
Reading Comprehension Question 2 of 6
Which of the following bacteria is primarily associated with dental caries?
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus mutans
- Lactobacillus acidophilus
- Porphyromonas gingivalis
- Escherichia coli
Answer: B. Streptococcus mutans
Explanation:
- A. Staphylococcus aureus: Incorrect. Staphylococcus aureus is not commonly associated with dental caries.
- B. Streptococcus mutans: Correct. Streptococcus mutans is a well-known acidogenic bacterium involved in the formation of dental caries.
- C. Lactobacillus acidophilus: Incorrect. Although Lactobacillus species can contribute to caries, Streptococcus mutans is more directly associated.
- D. Porphyromonas gingivalis: Incorrect. Porphyromonas gingivalis is associated with periodontitis, not dental caries.
- E. Escherichia coli: Incorrect. Escherichia coli is not typically involved in dental caries.
Reading Comprehension Question 3 of 6
What role do biofilms play in preventing pathogenic colonization in the oral cavity?
- They produce acids that kill pathogens
- They outcompete pathogenic microorganisms for resources and space
- They trigger an immune response that eliminates pathogens
- They secrete antimicrobial agents
- They disrupt existing biofilms
Answer: B. They outcompete pathogenic microorganisms for resources and space
Explanation:
- A. They produce acids that kill pathogens: Incorrect. Acid production can lead to dental caries but does not prevent pathogenic colonization.
- B. They outcompete pathogenic microorganisms for resources and space: Correct. The normal oral microbiota in biofilms competes with pathogens for resources and space, inhibiting their colonization.
- C. They trigger an immune response that eliminates pathogens: Incorrect. Pathogenic biofilms may trigger immune responses, but normal biofilms prevent colonization by competition.
- D. They secrete antimicrobial agents: Incorrect. While some biofilms might have antimicrobial properties, the primary mechanism here is competition.
- E. They disrupt existing biofilms: Incorrect. Biofilms themselves are structured communities, not disruptors of other biofilms.
Reading Comprehension Question 4 of 6
What dental disease is primarily caused by pathogenic biofilms eliciting an immune response leading to tissue destruction?
- Dental caries
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
- Oral thrush
- Halitosis
Answer: C. Periodontitis
Explanation:
- A. Dental caries: Incorrect. Dental caries are caused by acid-producing bacteria that demineralize tooth enamel.
- B. Gingivitis: Incorrect. Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that can be a precursor to periodontitis but does not primarily involve tissue destruction.
- C. Periodontitis: Correct. Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease caused by pathogenic biofilms that elicit an immune response, leading to tissue destruction.
- D. Oral thrush: Incorrect. Oral thrush is a fungal infection caused by Candida species, not bacterial biofilms.
- E. Halitosis: Incorrect. Halitosis (bad breath) can be associated with biofilms but is not a disease caused by tissue destruction.
Reading Comprehension Question 5 of 6
Which preventive approach is most effective in disrupting biofilm formation in the oral cavity?
- Using fluoride toothpaste
- Brushing and flossing regularly
- Drinking water after meals
- Chewing sugar-free gum
- Rinsing with mouthwash
Answer: B. Brushing and flossing regularly
Explanation:
- A. Using fluoride toothpaste: Incorrect. While fluoride toothpaste helps strengthen enamel, it does not directly disrupt biofilm formation.
- B. Brushing and flossing regularly: Correct. Regular brushing and flossing mechanically disrupt biofilm formation and remove dental plaque.
- C. Drinking water after meals: Incorrect. Drinking water can help rinse away food particles but does not effectively disrupt established biofilms.
- D. Chewing sugar-free gum: Incorrect. Chewing sugar-free gum can increase saliva production but is less effective in disrupting biofilms compared to brushing and flossing.
- E. Rinsing with mouthwash: Incorrect. Mouthwash can reduce bacterial load but is best used in conjunction with mechanical cleaning methods like brushing and flossing.
Reading Comprehension Question 6 of 6
What is the role of Streptococcus mutans in the development of dental caries?
- It produces extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)
- It outcompetes other bacteria for resources
- It elicits an immune response
- It metabolizes dietary sugars to produce acids
- It strengthens enamel
Answer: D. It metabolizes dietary sugars to produce acids
Explanation:
- A. It produces extracellular polymeric substances (EPS): Incorrect. While EPS production is a feature of biofilms, Streptococcus mutans is specifically known for its acid production.
- B. It outcompetes other bacteria for resources: Incorrect. This is a general feature of biofilms, not specific to Streptococcus mutans in the context of caries.
- C. It elicits an immune response: Incorrect. Streptococcus mutans does not primarily elicit an immune response; it causes damage through acid production.
- D. It metabolizes dietary sugars to produce acids: Correct. Streptococcus mutans metabolizes dietary sugars, producing acids that demineralize tooth enamel, leading to dental caries.
- E. It strengthens enamel: Incorrect. Streptococcus mutans contributes to enamel demineralization, not strengthening.
4. Quantitative Reasoning Test
Quantitative Reasoning Question 1 of 4
Evaluate the value of the unknown variable in the equation:
1/L = 13/8 + K/6
If L = 12,
K = __?__
- $$$ -9\dfrac{1}{4} $$$
- $$$ -9\dfrac{1}{2} $$$
- $$$ -9\dfrac{1}{6} $$$
- $$$ -9\dfrac{1}{24} $$$
The correct answer is A. (-9¼).
| 1/L = 13/8 + K/6 | (Substitute value of ‘L’ from the question). |
| 1/12 = 13/8 + K/6 | (Multiply LCD = 24 with the entire equation) |
| 24 * 1/12 = 24 * (13/8) + 24*(K/6) | (24/12 = 2; 24/8 = 3; 24/6 = 4) |
| 2 * 1 = 3 * 13 + 4 * K | |
| 2 = 39 + 4K | (Subtract ‘39’ from both sides of the equation). |
| 2 – 39 = 39 + 4K – 39 | |
| -37 = 4K | (Divide both sides of the equation by ‘4’). |
| (-37)/4 = K | (Convert improper fraction into a mixed fraction). |
| -(36 + 1)/4 = K | |
| -36/4 – 1/4 = K | |
| -9 – 1/4 = K | |
| K = -9¼ |
Quantitative Reasoning Question 2 of 4
The new lottery scratch card series guarantees a 1/10 chance of winning some monetary prize and a 1/2 chance that the win will be a substantial sum. If I buy 20 lottery scratch cards from the new series, how many substantial wins should I expect?
- 10
- 2
- 1
- 4
- 0
The correct answer 1 substantial win.
Explanation:
You can either accumulate the chances in order to find the answer or to calculate the chance of winning a substantial sum in advance.
Step by step:
Tickets bought = 20
Chance of winning tickets = 20 * 1/10 = 20/10 = 2
Chance of a substantial win = 2 * 1/2 = 2/2 = 1
In advance:
Chance of a substantial win = 1/10 * 1/2 = 1/20
Of the tickets bought = 20 * 1/20 = 20/20 = 1
Tips for a quick solution:
- Problems that deal with proportions, combinations, and probabilities, usually appear towards the end of the test. If this is your mathematical strong suit, and time is about to run out, you can guess the answers and move closer to the end of the test.
- Remember that the probability of two terms happening together is always lower than the probability of each of them happening without the requirement of co-occurrence.
Quantitative Reasoning Question 3 of 4
A 250-liter water tank is currently 36% full. How much more water is required to make it 50% full?
- 20 Liters
- 35 Liters
- 50 Liters
- 90 Liters
- 125 Liters
The correct answer is B.
Explanation:
The total capacity of the water tank = 250 liters
Given that 36% of the tank is full, the water missing that would make it 50% = 50% – 36% = 14%
14% of 250 Liters = 14% x 250 = (10% x 250) + (4% x 250) = (10/100 x 250) + (4/100 x 250) = 25 + 4 x 2.5 = 25 + 10 = 35 Liters
Solving Tip:
This question can be solved easily by a method of estimation, the remaining percentage of water needed to make it 50% full is 14%. Now, 12.5% is close to 14% and 12.5% of a value means that the value is divided by 8. So 12.5% of 250 liters = 250 / 8 = 31.2 liters which is closest to option ‘B’ the correct option.
Quantitative Reasoning Question 4 of 4
Parents of children studying at McArthur Primary School raised concerns regarding the nutrient level of the lunch menu served at school. What is the average of the total calories per meal served at McArthur School according to the table below?
| Meal | Portion Size | Vegetable Portion | Served on | Total Cals | % of Cals from Fats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turkey and Potatoes | 2 Pcs | 1.5 Cups | Mon, Thurs | 610 | 18.4% |
| Hamburger and Wedges | 1 Pcs | 2 Cups | Tues, Fri | 650 | 20.5% |
| Chicken and Beans | 3 Pcs | 1.5 Cups | Wed, Mon | 630 | 19.5% |
| Pizza and Salad | 4 Pcs | 3 Cups | Thurs, Tues | 530 | 26.2% |
| Spaghetti with Meat Sauce | 2 Cups | 2.5 Cups | Fri, Wed | 650 | 29.9% |
- 614
- 616
- 624
- 626
- 630
The correct answer is 614.
Explanation:
Focus only on the “Total Cals” column, as all other details are irrelevant. While the standard average formula is still
$$$(\text{sum of all elements}) \div (\text{number of elements})$$$, this direct approach may be too slow without a calculator and under time pressure. Instead, rely on faster methods to quickly determine the average.
- In order to calculate the average, you do not have to sum up all elements. You can also get to the average by averaging the distance of all elements from a certain middle element. This method helps you in calculating an average from smaller values – something that you should be able to do with ease even without using a calculator.
- Choose the middle element – if you reorder the elements by their value, find the value among the elements that would be in the middle. In our case – it is 630 (Chicken and Beans). Consider the median value as the temporary average.
- Find additional elements whose values are found equally above and beneath the middle value. These elements “cancel” one another, and thus the median value remains the temporary average. In our case, 650 (Hamburger) is 20 above 630, and 610 (Turkey/Potatoes) is 20 beneath 610. If those were the only elements to consider, you could have approved the middle element as the genuine average.
- The rest of the elements that can’t be paired – create a balance of their differences from the middle value. In our case:
- 650 is 20 greater than the middle value (630). Therefore, the balance is +20
- 530 is 100 lower than the middle value. Therefore, the balance is 20-100 = -80.
- As a final step, you need to divide the balance by the number of elements. You would add the product of this division to the middle value in order to get the genuine average. In our case:
- (The balance)/(number of elements) = -80/5 = -16
- Adding the product to the middle value –> 630-16 –> the average
- The average = 614
Sample Survey of the Natural Sciences Flashcards
Boost your Survey of the Natural Sciences prep with these key concept flashcards.
Well done!
You have completed the Sample Questions section.
The complete iPREP course includes full test simulations with detailed explanations and study guides.
‘…TESTS THAT ACTUALLY HELP’

In the first 30 minutes of use I have learned so much more than skipping along the internet looking for free content. Don’t waste you time, pay and get tests that actually help.
Richard Rodgers
January 28, 2020 at 7:49 PM