Test Breakdown & Sample Questions
The CSPDT exam is composed of 150 questions. 25 of them are pretests, and 125 of them are multiple-choice questions. You are provided with a total of 3 hours to complete them.
| Topic | Percentage Weight | Approximate Number of Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Roles and Responsibilities | 13% | 19 |
| Life Science | 9% | 13 |
| Decontamination and Disinfection | 19% | 28 |
| Preparation and Handling | 16% | 24 |
| Sterilization | 18% | 27 |
| Sterile Storage, Inventory Management, and Distribution | 11% | 16 |
| Patient Care Equipment | 6% | 9 |
| Ethics | 8% | 12 |
Roles and Responsibilities
The Roles and Responsibilities section is comprised of approximately nineteen questions covering 10 different topics. The topics include:
- Potential hazards at the workplace (e.g., EtO, wet floors, electrical outlets, Fires, fumes, body fluids, sharps, latex allergy, medical waste, and microorganisms).
- Compliance with manufacturer’s instructions for use (instrument cleaning, assembly, including chemicals, and sterilization equipment)
- Process of handling CJD-contaminated supplies, instruments, and equipment.
- Policies and procedures related to sterile processing functions (e.g., Infection Control, Disaster, Safety, incident reports, QA).
- Federal, state, and local guidelines, regulations, and standards (e.g., OSHA, EPA, FDA, CDC). Includes quarantine of implants, medical, SDS, and biohazardous waste.
- Function and workflow/traffic flow of the department of sterile processing.
- Processes for loaner instrumentation.
- Body mechanics and ergonomic considerations.
- Professional standards related to dress code and personal hygiene.
- Symbols and signs in packaging and IFUs.
Life Science
The Life Science section is approximately thirteen questions covering 5 different topics. The topics you are required to prepare for this section include:
- Microbiology concerning disinfecting, cleaning, and sterilizing, including biofilm
- Factors that contribute to disease transmission and methods of cross-transmission (e.g., blood, air, skin), handwashing, and the body’s defenses against infection.
- Microorganisms (e.g., viruses, fungi, bacteria, prions).
- Conditions for microbial growth (e.g., humidity and temperature).
- Basic physiology and anatomy.
Decontamination and Disinfection
The Decontamination and Disinfection section is 28 questions and covers 9 different topics. They include:
- Chemicals and their usage (e.g., environmental disinfectants, enzymatics, detergents, germicides, pH); knowledge of water quality and how it impacts detergents and rinsing.
- Factors that affect decontamination (e.g., water quality, water impurities, procedures, opening, and disassembling instruments and devices); frequency of changing enzyme sonic and soaking solutions; dilution of cleaning agents and detergent.
- Safe and secure usage of sterilant chemicals and high-level disinfectants (e.g., Ortho-phthalaldehyde, trophon,); PPE, expiration date, level of disinfection, temperature, rinsing, disposal of chemicals, concentration, contact time.
- Documentation for HLD, including MEC testing, items processed, solution temperature, QA testing of test strips, etc.
- Personal Protective Equipment and Standard Precautions utilized in the Decontamination Area, doffing, and donning PPE.
- Maintenance, testing, and operation of decontamination equipment (e.g., sonic lumen cleaners, washer/decontaminator, ultrasonic cleaners, cart washers, etc.)
- Loading and unloading process for sonics and washers, checking spray arms in washers, degassing of sonics, positioning of devices, etc.; testing of water quality and test results documentation.
- Methods of disinfecting, sorting, cleaning, and decontaminating lumens, instruments, rigid container systems, and equipment; manual cleaning protocols; processing tools used in chemotherapy agents; inspection, use, and maintenance of cleaning implements.
- Protection of devices from getting re-contaminated post-high-level disinfection.
- Basic care and handling of instruments and equipment while cleaning; including utilization of gloves when instruments are only sonic cleaned, and TASS precautions.
Preparation and Handling
The preparation and handling portion makes up almost 16% of the exam and covers 10 areas. The areas covered by preparation and handling include:
- Basic principles of set configuration and packaging, including labeling of sets, avoiding damage to sets, utilization of instrument air, use of tip protectors, and labeling of packages.
- Characteristics and use of packaging materials in the sterilization methods; includes Tyvek pouches, paper-plastic pouches, woven and rigid containers, dust covers, non-woven wraps, and inspection of containers/ packaging.
- Instrument anatomy and terminology (e.g., shanks, box locks, jaws, rings).
- Products and methods utilized to check on sterilization (e.g., chemical indicators, integrator) for packs, trays, and rigid containers.
- Handling and care of instruments to include the utilization of instrument handling of implants, lubricant, receipt of new instruments, storage of non-sterile instruments, etc.
- Package closures and tamper-evident seals (e.g., sterilization tape, its use, and application).
- Types of instrument construction (e.g., composition, finish).
- Functions and types of instruments (e.g., General, Orthopedics, Dental, power, GU, Neuro, Thoracic, Plastic, Cardiovascular, GYN, ENT, endoscopic, microsurgical, robotic), recognition of surgical instruments by name, how instruments are utilized (instrument usage in particular types of surgery).
- Inspection and testing process for surgical equipment and instruments, documentation of testing frequency, and insulation testing.
- Tray construction (e.g., size, density, weight, shape) and arrangement of instruments on sets.
Sterilization
The sterilization portion makes up almost 18% of the exam and covers 8 areas. The areas covered by preparation and handling include:
- Variety of sterilizers and sterilization methods (e.g., steam, gas plasma, vapor phase hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen peroxide-ozone, EtO, dry heat, etc.)
- Levels of sterility assurance, parameters for every sterilization methodology, and sterilization cycle (e.g., time, concentration, steam under pressure, temperature, humidity).
- Operation of sterilizers, including criteria of loading and unloading and process of all types sterilization, including cooling of packs.
- The cleaning process for various sterilization tools.
- Recall processes for goods sterilized inside the facility or purchased from an external manufacturer.
- Record keeping and lot control for all sterilization techniques, including date and lot number, documentation of load contents, etc., on the sterilization log, including types of lot control labels for all sterilization methods and event-related vs. time-related labels.
- Process for handling wet packs (e.g., resolution, causes).
- The sterilizers’ quality assurance testing; includes Bowie-Dick tests, leak tests, biological tests, etc., types, documentation of sterilization printouts and Purpose Interpretation, charts, chemical indicators, chemical integrators, and biological indicators, Including temp of incubators, documentation of chemical and biological indicators/integrators; keeping records neat, interpretation and signing of sterilizer printouts; saving records.; documentation of load information and contents (e.g., time, temperature, cycle, etc.).
Sterile Storage, Inventory Management, and Distribution
The sterile storage, inventory management, and distribution portion makes up almost 11% of the exam and covers 7 areas. The areas covered by preparation and handling include:
- Factors affecting shelf life (e.g., moisture, damage, excessive handling, and packaging materials).
- Sterile storage’s inventory management.
- Distribution systems (e.g., specialty carts, case carts, code carts).
- Receiving systems (e.g., breakout, corrugated boxes, containers).
- Shelving design and storage requirements (e.g., air exchange, environmental conditions -humidity, placement).
- Processes for tracking location and usage of specialty carts.
Patient Care Equipment
The patient care equipment makes up almost 6% of the exam and covers 3 areas. The areas covered by preparation and handling include:
- Collection, reassembly, and processing of patient care equipment. Tracking usage and location of patient care equipment.
- Disinfection, distribution, and storage of patient care equipment.
- Types of patient care equipment and their usage.
Ethics
The ethics portion makes up almost 8% of the exam and covers 2 areas. These include
- Professional behavior (e.g., disruptive behavior,’ non-compliance with dress code, theft, willful damage to equipment/property).
- Guidelines and/or processes that impact patients, employees, or environmental safety, compliance with regulatory standards, reporting instances of non-compliance, and best practices.
Did you know?
The CSPDT contains 150 Multiple choice questions (125 questions, and 25 pre-test questions). It covers eight sections, including Roles and Responsibilities, Life Science, Decontamination and Disinfection, and Sterilization. You need to get a score of at least 70% to receive a CBSPD certification.
Preparation Strategies
The following strategy will help ensure proper preparation for attempting the certification examination:
- Familiarize yourself with the exam objectives: Make sure you understand what the exam covers by reviewing the exam objectives. You can find the exam objectives on the certification provider’s website.
- Review the recommended study materials: The certification provider usually offers study materials that cover the exam objectives. These materials may include books, training courses, or online resources.
- Opt for an online course: Although it is not compulsory to register for the CSPDT course, it can help you pass the exam. Online courses tend to be preferred over offline ones, as most offline courses are pretty rigid, and you must alter your schedule according to the class timing. Online courses are quite flexible, and you can choose your preferred class times. Additionally, all your study material is saved on a cloud drive that you can access at any time.
- Create a study plan: Create a study plan based on the time you have available before the exam. Break the material down into manageable sections and allocate time for each section.
- Practice with sample questions: Use sample questions or practice exams to get a feel for the type of questions you can expect on the exam. This will help you to identify areas where you need to focus your study efforts.
- Join a study group or discussion forum: Join a study group or discussion forum to learn from others preparing for the exam. You can share study tips, ask questions, and discuss difficult concepts.
- Review regularly: Review regularly to reinforce what you have learned. This will help you retain information and ensures you are prepared for the exam.
Test Features
Test Fast Facts (tl;dr)
3-hour time limit
Total of 150 questions (125 test questions plus 25 pre-test questions)
The test includes eight sections, ranging from 8-30 questions.
MCQs are included for most items.
Administered online
Passing the test requires a score of 70% or higher.
No outside material is allowed at the test. However, you must carry an ID card.
To register for the test, you must pay a fee of $128. A $10 fine is applicable for late registrations.
Purpose of The Certification
CBSPD certification programs recognize individuals who meet competency-based standards that can be easily measured by professional members.
It also helps:
- To ensure the individual has the skills required to protect the public.
- To promote flexible endoscope processing personnel and healthcare sterile processing education.
- To spread awareness about the importance of continuing education for individuals working in the flexible endoscope processing professions and healthcare sterile processing.
- To encourage re-certification for individuals who were previously recognized as certified.
- To maintain a certification registry that is publicly accessible for flexible endoscope processing personnel and sterile healthcare processing.
- To encourage professional accountability for sterile healthcare processing and flexible endoscope processing personnel.

Possible to Make Changes in the Application
After registering for the CBSPD exam, you will receive a Registration Verification Notice via email or postcard. If you notice an error in your registration details, like name or address, inform the CBSPD office via call or email so they can update it. A candidate must take action immediately. Corrections can not be made after the 48-hour window provided. Candidates may also sign up for different exams than they initially registered for. (A fee of $10 for the exam change will be applicable).
Special Arrangements for Candidates With Special Needs
Special accommodation for a differently abled person can be requested from CBSPD. The arrangements will be provided following the federal Americans with Disabilities Act without extra charge. Candidates requesting special arrangements must contact the CBSPD office for further guidance.
Requests for any such accommodation must be made through a written application addressing CBSPD and must be received within four weeks before the examination date.
The written application must contain the following:
- A signed letter on office stationery from a medical professional who has examined the candidate’s condition, describing how they can be best accommodated.
- A handwritten letter from the candidate describing the requested accommodation.
Once the application is sent, CBSPD officials will thoroughly review it, and a final decision will be made. If your application is denied, you can either proceed with the examination without accommodation or get a full refund of your application fee.
Refund and Rescheduling Possible
Candidates who wish to withdraw from the examination may do so up to 2 weeks before the scheduled examination date. The withdrawal request must be made in writing by mail, e-mail, or fax with the reason mentioned. The request must be received in the CBSPD office by the provided deadline. You must pay a compulsory non-refundable $60 administrative fee. If the candidate does not follow the procedure, they won’t receive a refund.
If the candidate can’t take the exam initially, they may reschedule. Candidates must submit a transfer request in writing along with a $20 non-refundable transfer fee.
Re-Certification
Once you receive your certification, it will remain valid for five years. This decision was made by the CBSPD board after analyzing how often the industry experiences a significant change in technology/knowledge. To get recertified, you are required to accumulate 100 points for five years. Professionals are required to pay a fee of $125 to receive a recertification.
You are required to send in your recertification application six before the expiration date. You must also send in all your points approved by CBSPD.
Technical Facts
Eligibility Criteria
The CBSPD does not show any form of discrimination towards applicants based on their age, sex, race, religion, national origin, disability, marital status, or any other status protected by law. The examination is solely offered in English in the United States. Therefore, candidates must be able to interpret, speak, read, and write in English. To be eligible to take the exam, candidates must meet at least one of the requirements mentioned below before the deadline examination deadline:
- Completion of at least 12 months of full-time employment, or the same amount of part-time hours, in sterile processing and distribution activities, as verified by the candidate’s manager on the exam application.
- Completion of an SPD Training Course with a passing grade of 70 or higher, as evidenced by a copy of the certificate or grade from the instructor.
- The exam application requires verification by the candidate’s manager of related allied healthcare professional work and SPD activities in SPD, totaling at least six months of full-time employment or equivalent part-time hours.
- Completion of 12 months of healthcare product sales or service related to the SPD profession, as verified by the candidate’s employer on the exam application.
CSPDT vs. CRCST
| Certification | Issued by | Exam Structure | Required Practical Experience | Validity of the Certificate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSPDT(Certified Sterile Processing and Distribution Technician) | Certification Board for Sterile Processing and Distribution (CBSPD) | 150 multiple-choice questions in 3 hours. | At least one year of full-time experience | 5 years. |
| CRCST (Certified Registered Central Service Technician) | Healthcare Sterile Processing Association (HSPA, previously named IAHCSMM) | 150 multiple-choice questions in 3 hours. | At least 400 hours of hands-on experience | 5 years. |
CSPDT and CRCST are two different certifications in sterile processing and distribution.
CSPDT stands for Certified Sterile Processing and Distribution Technician. This certification is offered by the Certification Board for Sterile Processing and Distribution (CBSPD). It is designed for individuals with a high school diploma or equivalent and at least one year of full-time experience as a sterile processing technician or equivalent who have completed a sterile processing program or equivalent training in sterile processing and distribution. The CSPDT certification exam tests the candidate’s knowledge and skills in decontamination, sterilization, instrumentation, and medical terminology.
CRCST stands for Certified Registered Central Service Technician. This certification is offered by the International Association of Healthcare Central Service Material Management (IAHCSMM). It is designed for individuals with a high school diploma or equivalent and who have completed an accredited central service technician training program or have equivalent experience.
The CRCST certification exam tests the candidate’s knowledge and skills in decontamination, sterilization, instrument processing, and inventory management.
While both certifications focus on the sterilization and distribution of medical equipment, the eligibility requirements and exam content differ. It is important to carefully review the requirements and choose the certification that best fits your education, training, and career goals.
Language and Geography
The CBSPD does not allow the use of a reader for ‘English as a Second Language (ESL) candidates. The exam is exclusively offered in English in the United States. Candidates are expected to possess proficiency in interpreting, speaking, reading, and writing English. For countries where computer-based testing is unavailable through PSI Services LLC, including Spanish-speaking countries, the exams will be administered using a paper-pencil format at CBSPD-approved testing sites.
If a candidate requires a reader, PSI Services LLC will arrange for a professional to read the exam on the scheduled testing date, as requested and confirmed by the candidate. Any approved accommodations not related to the requirement for a reader will be provided by PSI Services LLC or the proctor approved by CBSPD. The CBSPD board of directors will carefully review and accommodate all reasonable requests for special testing services.
Results Scale and Interpretations
Exam Scores and Result Delivery Method
To pass the CSPDT certification exam, a candidate must achieve a scaled score of 70% or more. Upon completing the computerized exam, candidates testing in the United States will be given an official Pass/Fail notice. They will be directed to report to the proctor to obtain their score.
Those who pass will receive their certificates with an ID number within six weeks from the end of the exam window. Candidates who fail will receive a report at the testing center indicating their scores and subject areas of weakness. However, the CBSPD does not provide numeric scores for passing candidates, as the exam is designed to evaluate minimum competency and not differentiate between scores above the passing threshold. This policy is in place to prevent misuse of passing candidates’ scores.

International candidates testing via paper and pencil will receive their results via mail within eight weeks. Final results will not be disclosed over the phone or email by the testing agency or the CBSPD for security reasons. While the diagnostic report provided to failing candidates indicates their performance in each content domain, pass/fail decisions are not based on content domain-level scoring.
RAW and Scaled Scores
The CBSPD conducts standardized tests in multiple versions known as “forms.” These forms aim to evaluate the same knowledge and skills but with different questions. Test developers attempt to create questions of equal difficulty across forms, but some forms may be more challenging. As a result, the raw scores on different forms may not reflect the same level of knowledge or skill intended to be measured by the test. This would be misleading and unfair to test-takers who encountered more difficult questions.
To address this issue, testing agencies utilize “scaled scores” that compensate for differences in question difficulty. Each test form has its own “Raw-to-Scale conversion,” which provides the scale score corresponding to each possible raw score. CBSPD uses a 70 raw-to-scale score conversion and reports a scaled score of 70 or higher as a Pass, while a scaled score below 70 is reported as Fail. This ensures that scores are comparable across different test forms and that a given score indicates the same level of knowledge or skill, regardless of the test-takers form.
Notable Decline in CSPDT Scores in Recent Years
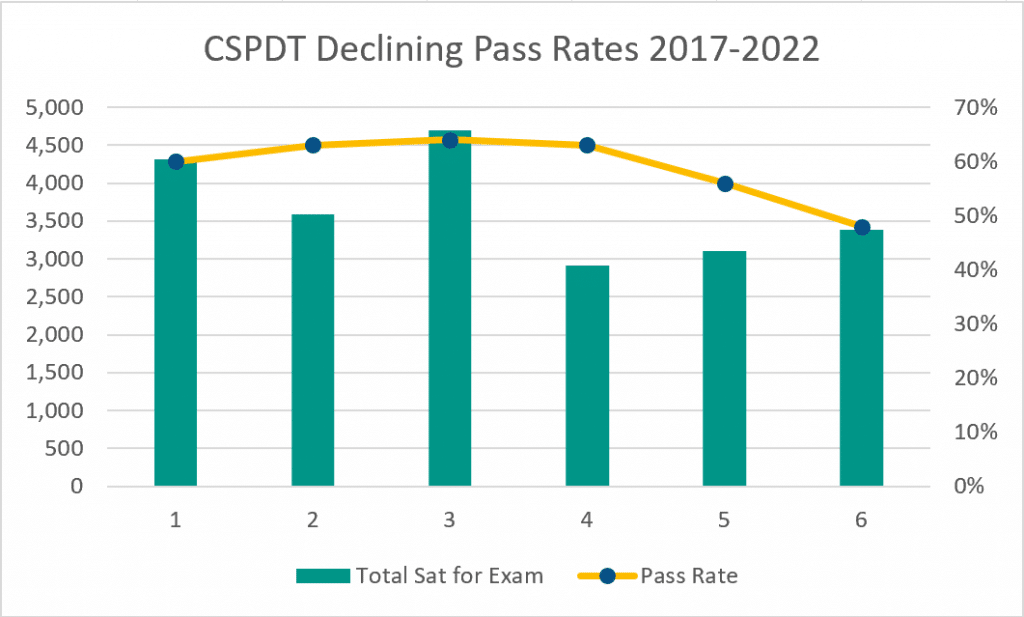
Over the past six years, there has been a notable decline in the pass rate for the Certified Sterile Processing and Distribution Technician (CSPDT) exam. In 2017, 60% of candidates passed the exam, a figure that rose to 64% in 2019. However, since then, the pass rate has steadily dropped, falling to 56% in 2021 and further down to 48% in 2022. This trend underlines the importance of adequate preparation before sitting for the CSPDT exam, as the decrease in the pass rate may suggest an increase in the difficulty level or a lack in thorough preparation among candidates.
Determining Cut Score
The Cut Score is used to establish the passing score for the certification exam by assessing the ability of the minimally competent test takers. The process for determining the Cut Score for the Technician exam is as follows:
- The exam is administered via computer to Committee members.
- The Cut Score meeting takes place within 7-10 days of the specific exam administration.
- After completing the exam, the Committee members rate each examination question based on the average applicant’s ability to answer it correctly.
- The actual test score is determined by analyzing all relevant data by the contracted psychometrician. This data includes the average educational level of candidates, their familiarity with exam taking, and their anxiety and nervousness.
- The Committee provides passing score analysis and recommendations to the CBSPD Board of Directors for approval.
- Once the Cut Score is approved, the exam can be scored.
- Exam scores from all administered exams are used to maintain a current passing score.
FAQs
CBSPD is a non-profit organization that provides certification programs for individuals working in the sterile processing and distribution field. CBSPD promotes and advances patient safety through certification, education, and research.
CBSPD offers several certification programs, including the Certified Sterile Processing and Distribution Technician (CSPDT), the Certified Flexible Endoscope Reprocessor (CFER), and the Certified Instrument Specialist (CIS).
The CBSPD CSPDT certification is for individuals working in sterile processing and distribution. The certification demonstrates a commitment to patient safety and ensures that individuals have the necessary knowledge and skills to perform their duties.
To be eligible for the CBSPD CSPDT certification, individuals must have a high school diploma or equivalent and at least 12 months of full-time employment in sterile processing and distribution. Alternatively, individuals can have a combination of education and work experience equivalent to 12 months of full-time employment.
The CBSPD CSPDT certification exam is a computer-based test with 125 multiple-choice questions. Candidates have three hours to complete the exam.
CBSPD CSPDT certification is valid for five years. To maintain certification, individuals must complete continuing education requirements and pass a renewal exam or demonstrate ongoing professional development.
CBSPD CSPDT certification demonstrates a commitment to patient safety and ensures that individuals have the knowledge and skills necessary to work in the sterile processing and distribution field. Certification can also lead to career advancement opportunities and increased earning potential.
CBSPD certification is valid for five years. To maintain certification, individuals must complete continuing education requirements and pass a renewal exam or demonstrate ongoing professional development.
CBSPD certification demonstrates a commitment to patient safety and ensures that individuals have the knowledge and skills to work in sterile processing and distribution. Certification can also lead to career advancement opportunities and increased earning potential.
Candidates can apply for CBSPD certification online or by mail. The application process varies by program but generally requires submitting educational and work experience documentation, payment of an application fee, and registration for the certification exam.
CSPDT Test Tips
Following are a few tips that may prove helpful on the exam day:
- Study regularly: Studying regularly over a longer period can be more effective than cramming right before the exam. Make a study schedule and stick to it to cover all the material thoroughly.
- Take care of yourself: Get enough sleep and eat healthy foods in the days leading up to the exam. Being well-rested and alert can help you perform better on the exam.
- Arrive early and be prepared: On exam day, arrive early to allow time to get settled and mentally prepared. Bring all necessary materials, such as identification and any permitted items, and follow the exam rules and regulations.
- Take advantage of the CBSPD Technician Study Guide: The CBSPD has developed a study guide to aid individuals in preparing for the Technician Certification Examination. This guide comprehensively covers all content areas and includes a discussion on test-taking techniques and sample questions. It should be noted that the study guide is not intended to serve as a textbook.
- Effectively manage your time: You will have limited time to complete the exam, so it is important to manage your time effectively.
- Read instructions carefully: Take your time and read all instructions carefully before beginning the exam. Doing so will ensure that you understand what is expected of you. It will help you avoid mistakes or misunderstandings.
- Stay focused and manage your time: During the exam, be focused and manage time wisely. Answer the questions you know first. Go back to the more challenging ones later. Do not spend too much time on a single question. Avoid rushing through the exam.
Administration
- Test Administrators: The CBSPD Board partners with PSI Services LLC, which is responsible for providing all the test administration services.
- Test Schedule: The candidate can schedule the date and time anytime during the selected week (window) specified on the application.
- Test Format: Computer-based Multiple Choice Exam. For countries where computer-based testing is unavailable through PSI, including Spanish-speaking countries, the exams will be administered using a paper-pencil format at CBSPD-approved testing sites.
- Test Materials: No external material is allowed in the examination center except for an ID card.
- Cost: $128 registration fees
- Retake Policy: No limits on the number of attempts, however, you must re-register and pay $128 every time you take the test.
Test Provider
The CSPDT test was designed by the National Institute for the Certification of Healthcare Sterile Processing and Distribution Personnel (NICHSPDP) which changed its name to the Certification Board for Sterile Processing and Distribution (CBSPD) in 2003. Apart from CSDPT, the organization also offers other certificates, including CSPM, CFER, CSIS, and CASSPT.
Resources
Disclaimer – All the prep material and information on iPrep are genuine and were created for tutoring only. iPrep has no affiliation with CBSPD, PSI Services LLC, or any other company mentioned.
Free CSPDT practice test: Get to know what the Certification Board for Sterile Processing (CBSPD) and Distribution’s Certified Sterile Processing and Distribution Technician (CSPDT) exam will be like by practicing with these sample questions:
Question 1 of 20
Topic: Cleaning, Decontamination, and Disinfection
Which one of the following is used in the manufacturing of bleach (decontamination product)?
- Ethyl alcohol
- Sodium hydroxide
- Sodium chloride
- Sodium hypochlorite
The correct answer is D.
Sodium hypochlorite is also known as bleach. Ethyl alcohol is used as a disinfectant while sodium hydroxide is used in the manufacturing of soaps. Sodium chloride is used in the treatment of patients who take fluids.
Question 2 of 20
Topic: Cleaning, Decontamination, and Disinfection
Which one of the following only shows cleaning agents?
- Detergents, degreaser
- Grease, detergents
- Abrasives, oil
- Acids
The correct answer is A.
They have surfactants and solvent chemicals as an ingredient.
Question 3 of 20
Topic: Cleaning, Decontamination, and Disinfection
Which one of the following is not a disinfection method?
- Chlorination
- Ionizing radiation
- Ozone
- Ultraviolet
The correct answer is B.
Ionizing radiation is a sterilization method. Chlorination, ozone, and ultraviolet are all used in the disinfection process.
Question 4 of 20
Topic: Cleaning, Decontamination, and Disinfection
You are cleaning your living room with a vacuum cleaner. Which statement below describes the correct order so that the rooms become clean?
- Vacuuming the floor and then dusting.
- Dusting the room and then vacuuming.
- Only vacuum as dust is eliminated
- Dust today and then vacuum tomorrow.
The correct answer is B.
Dust the room first and then vacuum to eliminate any dust that may have settled on other surfaces.
Question 5 of 20
Topic: Preparation & Packaging
How often should the warehouse be disinfected?
- Weekly
- Monthly
- Daily
- Anually
The correct answer is D.
You should disinfect annually as long as your warehouse is kept clean.
Question 6 of 20
Topic: Preparation & Packaging
What is the best temperature for flowers in the preparation and packaging room?
- 35°F-50°F
- 25°F-30°F
- 33°F-37°F
- 40°F-42°F
The correct answer is C.
33°F-37°F. Most flowers require a temperature between 33°F to 37°F to survive. However, tropical flowers and blossoms require temperatures above 50°F. Thus, the only option that falls between 33°F to 37°F is C as there is no option for above 50°F.
Question 7 of 20
Topic: Preparation & Packaging
What is the oldest packaging material in the world?
- Metal
- Plastic
- Tin
- Glass
The correct answer is D.
Glass is the oldest packaging material. It was invented over 5,000 years ago.
Question 8 of 20
Topic: Preparation & Packaging
What type of pressure is used to package food and beverage products?
- High pressure
- Low pressure
- High temperature
- Low temperature
The correct answer is A.
The use of high pressure eliminates harmful microbes from packaged food and beverages.
Question 9 of 20
Topic: Sterilization Process
Microorganisms are destroyed using a steam reaction known as?
- Third-order
- First-order
- Second-order
- None of the above
The correct answer is B.
First-order sterilization is a process of destroying microorganisms by steam.
Question 10 of 20
Topic: Sterilization Process
Which of the following processes only shows sterilization methods?
- Heat, radiation, chemical agents
- Pasteurization, high pressure, heat
- Ultrasonic, heat, pasteurization
- All of the above
The correct answer is A.
Heat, radiation, and chemical agents are sterilization processes. Pasteurization is a disinfection method so options B and C are incorrect.
Question 11 of 20
Topic: Sterilization Process
I want to use batch sterilization for medical tools. What is the best temperature and then state a reason for your answer?
- 100°C
- 102°C
- 112°C
- 121°C
The correct answer is D.
The high temperature has high pressure which is used to kill microorganisms.
Question 12 of 20
Topic: Sterilization Process
Sterilization deactivates different spores of organisms. Which one is referred to as control?
- Asexual spores Endospores
- Exospores
- None of the above
The correct answer is B.
Endospores have high resistance to heat. It is also one of the hardiest microbial contaminants.
Question 13 of 20
Topic: Patient Care Equipment
Which item of clinical equipment can you use to stop a person’s bleeding?
- Air bellow
- MRI
- Penlight
- Hemostat clamp
The correct answer is D.
It is a surgical tool that compresses blood vessels to stop bleeding.
Question 14 of 20
Topic: Patient Care Equipment
Tom just told the doctor he is having difficulty reading from the blackboard. Which tool will the doctor first use to examine Tom’s pupil dilation?
- Penlight
- Draw sheet
- Retinoscope
- VT 1 vision screener
The correct answer is A.
A penlight is a small flashlight with an LED bulb that doctors use to examine the condition of the pupil.
Question 15 of 20
Topic: Sterile Storage and Inventory Management
Which statement describes the minimum required SPD sterile storage conditions?
- High humidity but a controlled temperature
- Controlled humidity and temperature
- Controlled humidity and high temperature
- Controlled temperature and humidity but not traffic limit
The correct answer is B.
A controlled humidity of 30%-60% and a temperature of 18°C-23°C (64°C-74°C) is the minimum required temperature range. For option D, traffic needs to be limited. For option A, high humidity is not required and for option C, high temperature is not required.
Question 16 of 20
Topic: Sterile Storage and Inventory Management
What is the substance inside the ABC extinguisher?
- Ammonium phosphate
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
- Ammonium nitrate
The correct answer is A.
Ammonium phosphate is a flame retardant.
Question 17 of 20
Topic: Documentation and Record Maintenance
Which of documentation is not useful to a company’s staff?
- Goal-oriented documents
- Information-oriented documents
- Products’ how-to guides
- Reference documents
The correct answer is C.
How-to guides are useful to clients. Goal-oriented documents remind the staff of the company’s goals. Information-oriented documents share different information about the products and staff use it to confirm items. Reference documents are used by staff to refer to a certain clause.
Question 18 of 20
Topic: Customer Relations
A person comes into the office shouting about being overcharged for their subscriptions. What is the best way to handle the issue as you are registering a new client?
- Take the person to your supervisor.
- Say that the overcharged amount will be deducted from next month’s subscription.
- Inform the person you cannot cancel the receipt.
- Ask for their receipt and confirm their claim.
The correct answer is D.
Before giving any definite answer, ask for the receipt and confirm that their claim is true.
Question 19 of 20
Topic: ethics
A sterile processing technician discovers a discrepancy in the inventory count of a high-demand surgical instrument. The technician realizes that a coworker, who is known to be experiencing financial difficulties, has been taking these instruments home for personal use without authorization. What is the most ethical course of action for the technician to take?
- Ignore the situation to avoid conflict and potential repercussions.
- Confront the coworker directly about the unauthorized actions.
- Report the incident to the supervisor or department manager.
- Purchase replacement instruments to cover up the discrepancy.
The correct answer is C.
The most ethical course of action for the technician is to select option C) Report the incident to the supervisor or department manager. This ensures that appropriate action is taken to address the unauthorized actions and maintain patient safety. Options A, B, and D are incorrect. Option A ignores the problem, option B may escalate the situation, and option D involves fraudulent actions and does not address the issue properly.
Question 20 of 20
Topic: Life science
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of viruses?
- They are capable of independent reproduction.
- They require a host cell to reproduce.
- They can cause a wide range of diseases.
- They contain genetic material (DNA or RNA).
The correct answer is A.
Viruses are not capable of independent reproduction. They are obligate intracellular parasites that require a host cell to reproduce. Once inside a host cell, viruses utilize the cellular machinery of the host to replicate their genetic material and produce more virus particles. Viruses cannot carry out essential metabolic functions independently and rely on host cells for their replication and survival.
Sample Flashcards
About the course
Includes 14 practice tests (6 full-length simulations)
iPREP is a trusted test‑prep provider offering a full (CBSPD) Certification Board for Sterile Processing and Distribution’s Certified Sterile Processing and Distribution Technician (CSPDT) exam prep course, and on this page you can access free sample questions with full explanations and video walkthroughs.
You’ll get:
- Free real‑style CBSPD CSPDT questions
- Instant right/wrong feedback
- Step‑by‑step written solutions
Welcome to iPrep’s Certified Sterile Processing and Distribution Technician (CSPDT) prep course, designed to elevate your skills, boost your confidence, and prepare you to ace the CBSPD certification exam. This course is essential for those aspiring to a career in the Central Service (CS) department of healthcare facilities.
Our curriculum is structured to help you master the exam’s format, question types, and timing through a blend of educational lessons and realistic simulation tests. Here’s what you can expect:
- Interactive Lessons: Gain essential knowledge of key topics such as decontamination, sterilization, and patient care equipment. These lessons are designed to help you decode the concepts and techniques crucial for exam success.
- Expert Tips and Strategies: Learn effective methods for handling different question types. Detailed explanations accompany each question to help you grasp test strategies and avoid common pitfalls.
- Full-Length Simulation Tests: Experience six practice exams designed to replicate the real CSPDT test, complete with time constraints and question difficulty. These tests will condition you for test-day pressure, ensuring that you are ready to perform at your best.
- Performance Insights: After each simulation, you’ll receive detailed feedback and performance comparisons with other test-takers to help you identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Our course emphasizes exam readiness, not just content mastery. While it won’t teach every topic from scratch, it’s tailored to make you more comfortable with the CSPDT exam structure, giving you a competitive edge.
20
Learning hours
14
Practice tests
900
Questions
400
Flashcards
Skills you will learn
Exam Strategy
Time Management
Question Analysis
Score Improvement
Curriculum
- Course Introduction
- CBSPD-CSPDT Certification Exam Format
- Section 1 – Roles and Responsibilities
- Section 2 – Life Science
- Section 3 – Decontamination and Disinfection
- Section 4 – Preparation and Handling
- Section 5 – Sterilization
- Section 6 – Sterile Storage, Inventory Management, and Distribution
- Section 7 – Patient Care Equipment
- Section 8 – Ethics
- Preparation Strategies and Test-Day Tips
- Six Full-Length CSPDT-Style Simulation Tests
- Course Conclusion
Customer testimonial

Amazing, so glad I found iPREP. I didn’t sign up for a traditional course at a college. I plan on getting certified for cheaper because I don’t have the money, and iPREP is helping me tremendously.
Chester Larsen
November 25, 2024 at 1:15 PM
Reviews

Daniel A****
August 2, 2025 at 11:00 PM
This service kicks butt! they give you everything you need to ace an exam. You do need an in-person sterile processing school to teach you the initial concepts, but this will get you ready for the exam itself. No complaints, totally worth the $30 for the responsiveness and interface.

jon l*
July 18, 2025 at 12:32 AM
The test questions don't really cover the sterilization techniques which is a large part of the exam. Sort of a disappointment. I was able to find better study material elsewhere.

Tammy D******
July 12, 2025 at 6:04 PM
I am trying to study for exam and I cant get to the part where they have multiple choice. All I see is flash cards. I don't want that. I paid 40 dollars for this . I need the multiple choice section which I had before ,

iPrep
July 12, 2025 at 6:17 PM
Hi Tammy. In the "Full-Length CSPDT-Style Simulation Tests" unit we have plenty of tests for you. Good luck on your test!

Lolita D****
April 25, 2025 at 1:07 AM
Thank you iPrep team!!! Whoever put this exam together, they knew just what they were doing. I love how the material of sterile processing regarding surgical instuments, medical devices, is well explain, emphasizing the importance of properly cleaning both simple and complex designed instruments, especially flexible scopes. Without cleaning correctly, sterilization can not be effective. Yes, I am on the same team as we want to reduce HAI and SSI from occuring in patients . Our goal is for the safety of patients.

Ashanti R*************
January 29, 2025 at 3:33 PM
This course helped me prepare for my certification in ways I could have never imagined. I will definitely use this site in the future when studying for my BS in Healthcare Admin/Mgmt.

Isabel E******
January 22, 2025 at 11:21 PM
This program is excellent to prepare you for the CSPDT exam! Thank you to iprep for this amazing program. Thank you so much!

Zandra L*****
January 19, 2025 at 7:34 AM
Really like the material, let’s see how it goes for me. First time to take it nervous but feel confident with this material

Jazsmin L******
January 17, 2025 at 9:12 PM
Iprep has helped me study so much for my upcoming exam, I was so nervous before but I'm starting to feel more confident! Thank you!

Jewel H*****
January 12, 2025 at 11:43 PM
This is really going to help me pass the test. It has everything I've been looking for. Thanks for existing