iPREP is a trusted test‑prep provider offering a full TExES Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities (PPR) EC-12 (160) computer-adaptive exam prep course, and on this page you can access free sample questions with full explanations and video walkthroughs.
You’ll get:
- Free real‑style PPR questions
- Instant right/wrong feedback
- Step‑by‑step written solutions
Test Breakdown with Sample Questions
Computer adaptive testing is utilized for the Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities EC-12 (160) exam. Here’s an example of how it works:
The initial question is categorized as having a moderate difficulty level, and the subsequent question may vary in complexity depending on your response. If you answer the first question correctly, the following question will become more challenging. Conversely, if you answer incorrectly, the subsequent question will be easier.
The questions on this exam are assigned scores ranging from 100 to 300. The difficulty of a question is indicated by its rating; for instance, a question with a rating of 210 will be more demanding than one with a rating of 140.
The exam’s content is organized into comprehensive content areas known as Domains, which are briefly outlined in the table below:
| Domain Title | Approx Percentage Of The Test | Standards Assessed |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Designing Assessment and Instruction to Promote Student Learning | 34% | Pedagogy and Professional Responsibility EC–12: I |
| 2. Creating a Positive, Productive Classroom Environment | 13% | Pedagogy and Professional Responsibility EC–12: II |
| 3. Implementing Effective Responsive Instruction and Assessment | 33% | Pedagogy and Professional Responsibility EC–12: I, III; Technology Applications: I-VII |
| 4. Fulfilling Professional Responsibilities and Roles | 20% | Pedagogy and Professional Responsibility EC–12: IV |
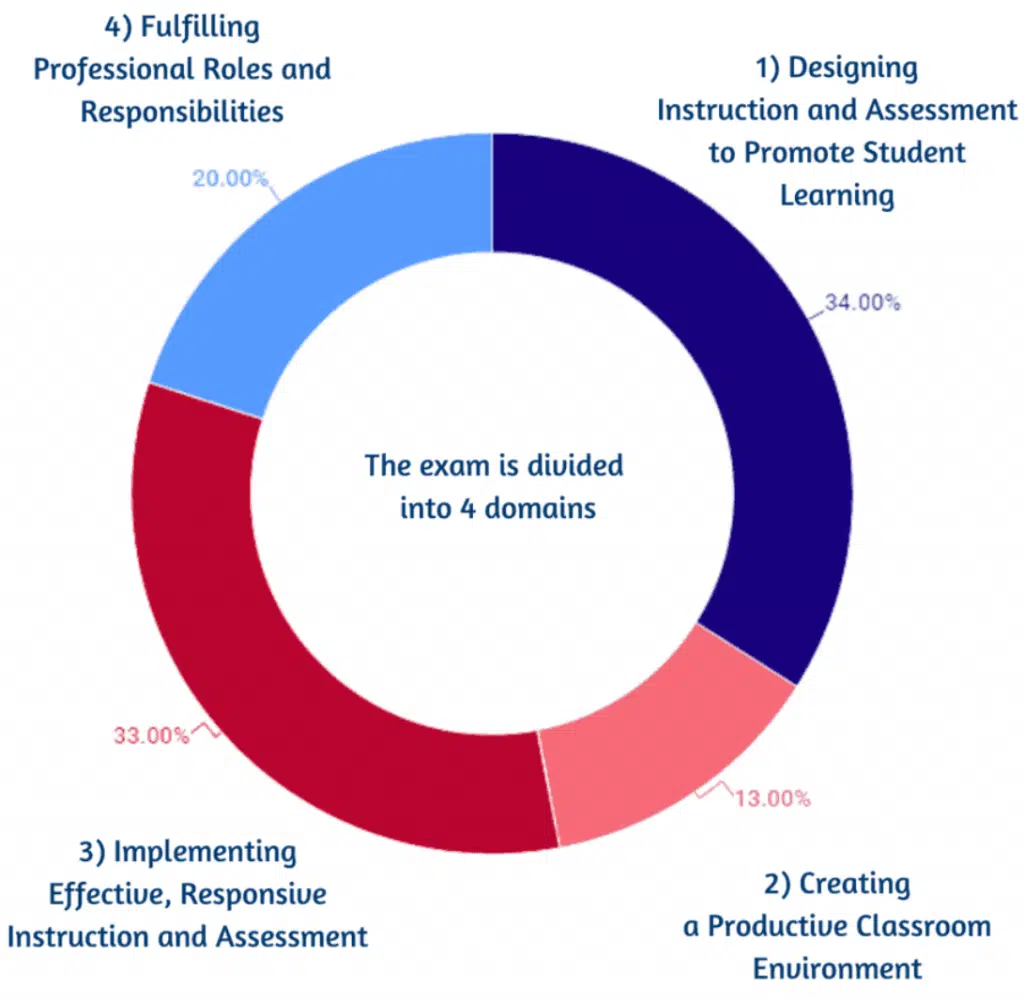
PPR Exam Domains, Source: Texas Teachers of Tomorrow
Each domain covers one or more of the educational standards in this discipline.
A collection of competencies further defines the material inside each area. Each skill is made up of two main components:
- The competence statement outlines the general knowledge and skills that an entry-level educator in this sector in Texas public schools should possess.
- The detailed descriptions of the knowledge and abilities are testable in the descriptive statements.
Understanding the Domains in Detail:
I. Designing Instruction and Assessment to Promote Student Learning (34%)
There are four competencies that make up the questions of this domain:
Competency 1: Recognizing various human developmental processes, as well as designing instruction that inspires pupils and considers their developmental requirements.
Competency 2: Knowing how to develop and construct exams that are sensitive to a wide range of students and their characteristics, as well as comprehending diversity in a group of students.
Competency 3: Knowing how to create assessments and instructions that are effective and coherent and are based on relevant learning objectives.
Competency 4: Recognising the elements influencing student learning and developing efficient, engaging, and pertinent lesson plans.
Domain 1 Sample Question
After every marking period, Mr. Johnson, a middle school teacher, encourages students to assess their academic collections, encompassing a range of tasks from every subject. For each subject, he prompts students to highlight one particular strong point and one aspect that requires enhancement in their work. By employing this strategy, Mr. Johnson is chiefly assisting students in developing which of the following?
- Communication skills
- Time-management skills
- Goal-setting skills
- Creative thinking skills
The correct answer is (C) Goal-setting skills.
Explanation:
Mr. Johnson’s approach promotes self-reflection and helps students identify both their strengths and areas that need improvement in their work for each subject. By doing so, students are better equipped to set academic goals for themselves. It encourages self-directed learning and personal development.
Answer (A), Communication skills, while valuable, is not the primary skill being developed by this practice. While the students may discuss their findings with others, the focus is on introspection and self-evaluation.
Answer (B), Time-management skills, while critical in an academic setting, is not the main skill being developed in this scenario. The activity doesn’t explicitly involve planning and organizing time.
Answer (D), Creative thinking skills, is not the main focus of this activity. While it’s possible that reflecting on their work might spur some creativity, the main purpose is to identify strengths and weaknesses to create goals for improvement.
II. Creating a Positive, Productive Classroom Environment (13%)
Two competence make up the questions in this domain:
Competency 5: Understanding how to establish a secure, productive environment that promotes learning, excellence, and equity in the classroom.
Competency 6: Knowing how to set up a structured and effective learning environment.
Domain 2 Sample Question
A teacher assigns a project to the class and outlines the correct steps for collecting the required materials and for putting the materials back in their appropriate spot after utilization. A key objective of outlining these steps is to
- enhance students’ organizational skills.
- set high standards for the students.
- foster students’ problem-solving skills.
- create avenues for student collaboration.
The correct answer is (A) enhance students’ organizational skills.
Explanation:
By instructing students on how to gather necessary materials and return them after use, the teacher is encouraging orderliness and planning. These skills are central to good organizational practices, helping students manage their resources effectively, and maintaining a clean and efficient learning environment.
Answer (B), set high standards for the students, while potentially correct, is not the primary purpose of the procedures in this context. High standards generally refer to academic or behavioral expectations rather than organization of materials.
Answer (C), foster students’ problem-solving skills, is not the primary goal here. While managing resources could involve some problem-solving, the instructions provided by the teacher are more focused on promoting organization than independent problem-solving.
Answer (D), create avenues for student collaboration, is not the primary purpose of these instructions. While students might work together to gather and return supplies, the main purpose of the procedures is to promote individual organizational skills.
III. Implementing Effective, Responsive Instruction and Assessment (33%)
There are four competencies that make up the questions in this domain:
Competency 7: Recognising and using effective communication in a range of educational contexts.
Competency 8: Giving students the right instruction will include them in the learning process.
Competency 9: Effectively utilizing technology to plan and provide instruction
Competency 10: Monitoring student progress and performance, giving quick feedback to students, and acting adaptably in response to encourage learning.
Domain 3 Sample Question
In the middle of a lecture, a student is inadvertently clicking a pen, causing a disturbance to a few neighboring students. To handle this situation most efficiently with the least interruption to the lecture, the teacher should:
- raise their voice to overshadow the noise of the clicking
- halt the lecture and request the student to stop clicking.
- establish eye contact and signal the student to cease.
- approach and confiscate the student’s pen.
The correct answer is (C) establish eye contact and signal the student to cease..
Explanation:
This method effectively communicates the teacher’s desire for the student to stop the distracting behavior without having to interrupt the flow of the lecture or drawing excessive attention to the student. Eye contact and nonverbal cues are powerful communication tools in a classroom setting.
Answer (A), raise their voice to overshadow the noise of the clicking, might not address the issue effectively and could lead to an escalation of noise levels in the classroom, creating more distractions.
Answer (B), halt the lecture and request the student to stop clicking, while it directly addresses the issue, it disrupts the lecture and draws undue attention to the student, which can be embarrassing or shaming.
Answer (D), approach and confiscate the student’s pen, may seem too invasive or punitive for such a minor infraction and could potentially escalate the situation or embarrass the student. Furthermore, it might disrupt the lecture more than necessary.
IV. Fulfilling Professional Roles and Responsibilities (20%)
Three components make up the questions in this domain:
Competency 11: Effective communication and interaction with families, including understanding the value of family involvement in a child’s education.
Competency 12: Developing professional knowledge and abilities by engaging in a range of professional activities and effectively communicating with other members of the educational community.
Competency 13: Recognising and upholding the ethical and legal obligations of educators.
Domain 4 Sample Question
A high school math teacher observes that a student’s performance has slightly declined since the introduction of the algebra unit. To optimally communicate with the student’s parents, the teacher should:
- motivate the student to bring up the matter with their parents
- wait for the parents to express any concerns first.
- append a note for the parents in the upcoming performance report.
- promptly contact the parents regarding the situation.
The correct answer is (D) promptly contact the parents regarding the situation.
Explanation:
This method of communication is the most proactive and immediate. It provides the parents with a direct update on their child’s academic performance, allows for immediate response and dialogue, and establishes a collaborative relationship between the teacher and parents. This would help in the development of potential strategies to improve the student’s understanding and performance in the algebra unit.
Answer (A), motivate the student to bring up the matter with their parents, puts the responsibility of communication on the student and might not ensure that the message is delivered effectively or at all.
Answer (B), wait for the parents to express any concerns first, is a passive approach and does not reflect the teacher’s active role in a student’s education. It may result in a delay in taking action to assist the student.
Answer (C), append a note for the parents in the upcoming performance report, is a more delayed approach and might not provide an opportunity for immediate dialogue and intervention. The progress report might not be due for several weeks, and the student could continue to struggle in the meantime.
Did you know?
The TExES Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities (PPR) EC-12 (160) computer-adaptive exam comprises 100 multiple-choice questions and must be completed within a time limit of 4 hours and 45 minutes. Some questions on the exam may not affect the final score, with the number of scored and unscored questions varying.
Preparation Strategies
Your success on the day of the PPR test depends not just on how much time you spent practicing but also on whether you did it correctly. It’s wise to check in periodically to determine if your learning is having any positive effects. To assess your progress, taking PPR practice exams is one of the most efficient methods to achieve this. Practice exams are helpful since they highlight your areas for growth. Pay close attention to these three categories of questions every time you take a free Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities EC-12 exam practice test:
- The wrong-answer questions
- The ones that required guessing, even if you were correct.
- The ones that you found challenging or time-consuming to finish.
This will show you exactly where you are weak and where you need to spend more time studying. Why did you have problems answering each of these questions? Was it because you didn’t grasp the subject matter? Was it a result of your forgetting the vocabulary? Do you need more practice answering questions of this nature to improve your speed and confidence? As you go back and examine the information, go further into those issues to see how you might enhance your weak areas.
- Answer Explanations: Additionally, many PPR (160) practice tests, like the one offered by iPrep, have a section on the answer choices. Reading the explanation and concluding that you fully understand the idea might be tempting. However, an explanation often addresses a portion of the question’s larger context. Even if the explanation sounds clear, thoroughly research each idea connected to the issue until you are confident you have a firm grasp of it.
- Comprehend Each Topic: As you go along, remember that the PPR practice test is just that: practice. Memorizing the questions and answers won’t help on the actual test day as it is very unlikely to have any same questions. You won’t be fully prepared for the real deal if all you know is the correct answers to the sample questions. Thoroughly study the concepts until you fully understand them, and then you’ll be able to answer any question that shows up on the test.
- Remove Limitations: With plenty of time to spare, take the first test while having your notes and the TExES Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities study guide nearby. Spend some time practicing the techniques you’ve learned.
- Time Yourself: Take the second practice exam, “open book,” as well, but set a timer and practice managing your pace to finish it in the allotted amount of time.
- Simulate Test Day: Take all additional exams as if they were actual exams. Put your study stuff away and set a timer. As you sit at a desk or table in a quiet place at the exam center, picture yourself answering questions as quickly and precisely as possible.
- Keep Practicing: Till you run out of practice exams or it’s time for the real examination, keep taking practice tests regularly. Since your mind will be ready for the test day schedule and pressure, you’ll be able to focus on memorizing the material you’ve learned.
Here’s a great piece of advice from a test taker:
“#1 piece of advice I was given, and echo it to you: just consider every question’s scenario as taking place in a “perfect world” classroom.”
Source: Reddit/sbloyd
Test Features
Academic Language and How It Intersects With the PPR Exam
Academic language refers to the specialized vocabulary, grammatical structures, and discourse patterns that are commonly used in academic settings, such as universities, research institutions, and scholarly publications. It encompasses the language skills and knowledge required to comprehend and produce complex texts, engage in academic discussions, and effectively communicate ideas within a specific discipline or field of study.
The PPR (Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities) Exam, on the other hand, is a teacher certification exam administered in some states or regions. It assesses a candidate’s knowledge and understanding of pedagogical principles, professional responsibilities, and educational practices necessary for effective teaching. While the specific content and format of the PPR Exam can vary, it typically includes questions related to educational theories, teaching strategies, classroom management, assessment techniques, and legal and ethical considerations in education.
The intersection between academic language and the PPR Exam lies in the expectation that aspiring teachers possess strong academic language skills and an understanding of how to support their students in developing these skills. Here are a few key points to consider:
Comprehension of Exam Materials: The PPR Exam often presents candidates with complex passages, case studies, or scenarios that require careful reading and analysis. Candidates should be able to comprehend and interpret these materials accurately, which involves understanding academic language and specialized terminology specific to the field of education.
Written Expression: Candidates are typically required to provide written responses to essay questions or demonstrate their ability to construct coherent written arguments. Effective written expression in an academic context involves using appropriate vocabulary, sentence structure, and organizational patterns to convey ideas clearly and succinctly.
Communication with Students: As teachers, candidates are expected to model and teach academic language skills to their students. They are expected to be able to explain concepts using clear and concise language, scaffold learning experiences, and facilitate discussions that promote critical thinking and academic discourse.
Differentiation and Accessibility: The PPR Exam may assess candidates’ understanding of how to make academic content accessible to diverse learners, including English language learners (ELLs) and students with special needs. This includes strategies for modifying language, providing explicit instruction on academic vocabulary, and utilizing visual aids or other supports to enhance comprehension.
Professional Development: The PPR Exam may also cover topics related to ongoing professional development, including the importance of staying abreast of research and best practices in education. This involves reading and understanding academic literature, attending conferences, and engaging in professional dialogue using appropriate academic language.
Academic language skills are crucial for success in the PPR Exam, as they are integral to comprehending exam materials, expressing ideas effectively in writing, communicating with students, differentiating instruction, and engaging in ongoing professional development. Aspiring teachers must demonstrate not only their pedagogical knowledge but also their ability to engage with and support the academic language demands of their future classrooms.
Approaching the Selected-Response Question
The PPR test features selected-response questions designed to analyze the knowledge you have about the content described in the test framework. In the majority of the scenarios, it’s expected for you to showcase more than your ability to recollect factual information. You may be instructed to think critically about the data, have a proper analysis, carefully consider it, and compare it with other pieces of information you have or provide your judgment about the same.
Interactive question types may also be employed on tests. Leveraging technology, these questions evaluate knowledge and abilities that conventional single-selection selected-response questions are unable to capture. Read the instructions carefully if you notice a format you are unfamiliar with. You will always receive explicit information on how to reply in the directions.
Leaving questions unanswered is not recommended, as no negative marking is applicable. The question for which you do not mark an answer would be considered incorrect. Your final score is determined by the number of questions correctly answered by you.
Although there’s no penalty for wrong questions, you should be very cautious while approaching unfamiliar question formats, as your chances of passing depend on the number of questions answered correctly. Therefore, even if you plan to use guesswork for the questions you are familiar with, it should be calculated and random.
The majority of questions need you to select one answer from a selection of choices by clicking an oval. You may be asked to answer in other situations by:
- Picking all that applies: You could be required to select every response choice for a particular question.
- Entering text into an entry box: If the answer is a number, you may be required to provide a numeric response, or if the exam has an on-screen calculator, you may be required to enter the result that was computed. Multiple places to enter an answer are possible for specific questions.
- Clicking checkboxes: If multiple options may be chosen from a group of replies, you can be requested to do so rather than an oval.
- Clicking parts of graphics: A few questions require you to select your response by clicking on specific locations on a visual, such as a map or chart, instead of picking it from a list.
- Clicking on Sentences: Choosing your response by clicking on a single or many phrases from the reading passage may be required in questions involving reading passages.
- Drag & drag response options into the screen’s “targets”: You may be required to choose an answer from a list and drag it to the proper spot in a table, text paragraph, or image.
- Selection of alternatives from a drop-down menu: For this kind of inquiry, you will be required to choose the proper response or answers by doing so (for example, to finish a phrase).
Keep in mind that you will receive explicit instructions on how to reply to each question.
The suggested approach for the questions of unfamiliar format includes the following:
- Read the questions critically and carefully.
- Pay attention to details like What the question is asking and what situation it describes.
- Eliminate the responses that are quite obviously incorrect.
- Select the correct response
- Mark your answer
Here’s what a reddit user has to say about the task:
“I took and passed the PPR early 2021, the Texas preparation practice test is useful and would recommend to look at. Try different quizzets to study vocabulary. I got a total of 62 questions correct (all different from each competency) scored a a little higher than 240. “
Source: Reddit/Teacher_girl2
Reschedule or Cancelation of PPR Exam
Up to 48 hours before the planned appointment, you can reschedule, postpone, or withdraw from a test. This policy allows applicants to change their exam plans in a fair amount of time. It acknowledges that unexpected events or changes in personal circumstances can occur and call for a revision in the exam timetable.
Candidates are given the option to change their plans without facing the consequences or risking their chances of passing the exam by allowing them this window of time. The exam slot may be forfeited, or additional costs may apply if changes are made after the 48-hour window, depending on the exam board’s regulations. Thus it is vital to remember that observing the deadline is essential.
Testing Accommodations
Individuals with a verified physical, learning, or cognitive disability may get testing accommodations. Access for wheelchairs, amenities for better vision, comfort items, pauses for using the toilet or taking medicine, etc., are provided without prior authorization. Additional accommodations must have administration and testing center approval ahead of the exam.
You will be questioned about your need for alternative testing arrangements when you register. If you require any of the aforementioned accommodations or any other accommodations, please choose yes. During the TExES exam registration procedure, there will be a place for you to provide any extra accommodations that need to be approved.
Technical Facts
PPR Fast Fact
- There are 100 multiple-choice questions on the TExES Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities or PPR EC-12 (160) computer-adaptive exam, which has a time constraint of 4 hours, 45 minutes. The test also includes questions that are part of the 100 questions that have no effect on your score.
- Multiple Choice Questions for most items.
- Completing the PPR Exam is often required for obtaining a teaching certificate or license.
- 240 is the passing score for the PPR exam.
- Individuals with a verified physical, learning, or cognitive disability may get testing accommodations.
- Up to 48 hours before the planned appointment, you can reschedule, postpone, or withdraw from a test.
- No penalties for wrong answers
PPR Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria for the TExES Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities (PPR) EC-12 exam may include the following requirements:
- Education: You must have completed a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution.
- Teacher Certification Program: You should have completed an approved teacher certification program. The program can be completed through a traditional university-based program or an alternative certification program.
- Teacher Preparation: You must have completed the required teacher preparation coursework as part of your teacher certification program. This includes coursework related to pedagogy, teaching methods, classroom management, and professional responsibilities.
- Criminal History Review: You will likely be required to undergo a criminal history review, which may include a fingerprinting process and background check. This is to ensure the safety and well-being of students.
- Additional Requirements: It’s important to note that eligibility requirements may slightly vary depending on the specific state or district where you are seeking certification. It is recommended to consult the official website of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) or the State Board for Educator Certification (SBEC) for the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding eligibility criteria.
Registration Process
Registering for the PPR or any other TExES exams can be done simply with four easy steps.
- Step 1: The 1st step is to register for a Texas Education Agency (TEA) online account. Your TEA ID will be sent to you after your account has been created. You should save a copy of this ID for your records since it is necessary to finish the registration procedure.
- Step 2: Sign up for a Pearson account on the Texas Educator Certification Examination Program. To sign up for this account, you must have a TEA ID. You may register for, schedule, reschedule, and access your TExES exam results using this account.
- Step 3: Sign up for a test or tests. Make sure you have the necessary authorization from TEA or your program/agency before signing up for a particular exam. You will choose the exam, respond to background questions, and turn in any necessary documentation for alternate testing arrangements during TExES registration. Only upon enrollment will you be given the chance to choose to have your test results sent to you. All TExES tests including PPR test have a $116 testing price. You will have 170 days from the time you register for your exam to book a testing session.
- Step 4: Make an appointment for the exam. Choosing your slot on a particular day and time distinguishes this from signing up for an exam. You can use a seat availability tool to find the time, place, and date that work best for you.
Retake Policy
Don’t give up if you don’t succeed the first time. The TExES PPR Exam may be retaken up to a maximum of five times. It’s critical to keep in mind that passing licensing examinations can be difficult for many educators and that this does not say anything good about your effectiveness as a teacher.
You must wait at least 45 days after your prior try before you may repeat the test, allowing you plenty of opportunity to review and improve your knowledge and abilities. You will also need to re-register, which involves paying a fee and taking the exam. Accept the possibility for development and make use of the resources at your disposal to increase your chances of success.
Results Scale and Interpretations
TExES PPR Passing Score
The TExES PPR test scores range from 100 to 300, with 100 being a failing grade (0%) and 300 representing a passing grade (100%). 240 is the PPR passing score. Making an informed guess when you are unsure of the correct response is acceptable since you will not be penalized for giving the incorrect answer. Each accurate response receives one raw point on a scale of ten for selected-response (multiple choice) questions. Out of all the selected-response questions, the total raw score represents the proportion of right answers. The grade for constructed-response questions varies with the number of test participants.
Understanding Your Score
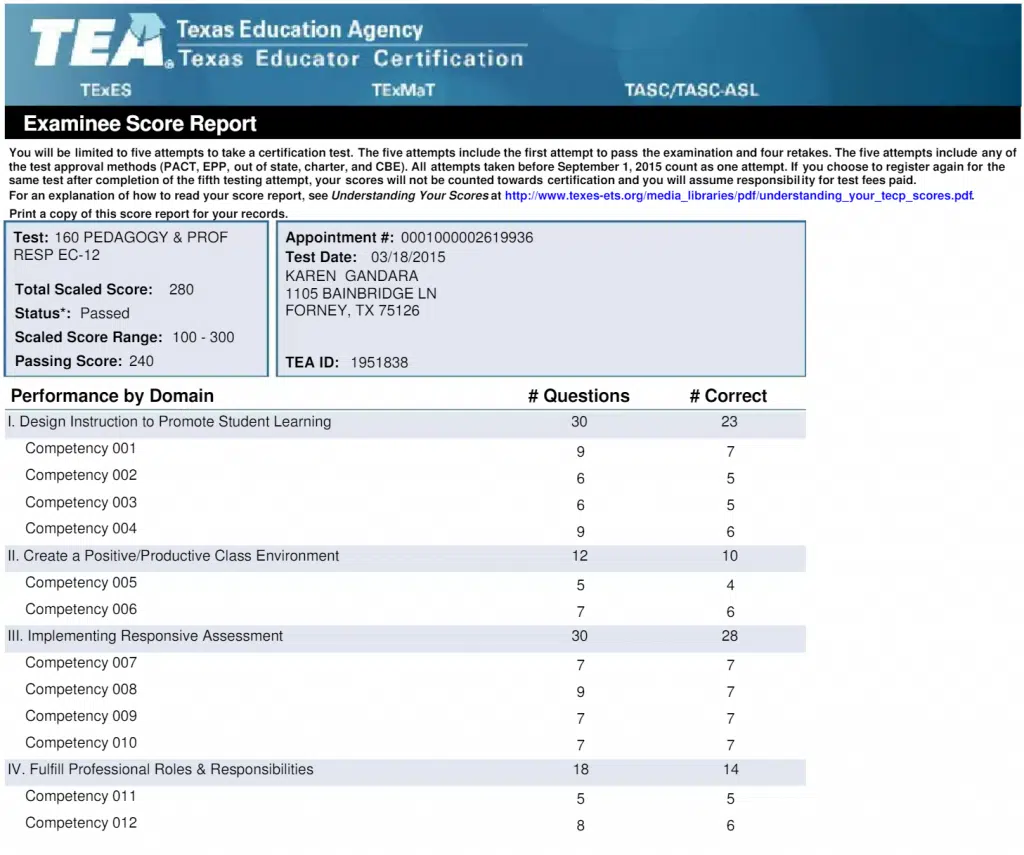
The four components of your PPR score report include overall test performance, performance by competency and domain, and holistic (constructed-response) scores.
- Section 1. Total Test Performance: Your pass or fail status, total scaled scores, scaled score range, and minimum passing scores are all included in Section 1 of the test.
- Section 2. Performance by Domain: The number of scored questions answered adequately for each of the main subject areas on the test will be listed. From one test to the next, a domain may have a different number of scored questions. Due to their limited scale and inability to fully capture your knowledge in each subject area, these ratings should be interpreted with care. This component does not have a pass/fail grading system, but it is useful in assessing your total result.
- Section 3. Performance by Competency: The individual competences within a domain are listed in this section. The amount of scored questions and successfully answered questions will be provided, similar to the performance by domain section. Once more, exercise caution while analyzing these tiny scale scores. They are meant to make your total score easier for you to grasp.
- Section 4. Holistic Scores: In this part, a score scale with four categories—complete knowledge, general knowledge, limited or no knowledge, and unscorable—will be displayed. Based on this table, answers will be graded using a number or letter system.
Here’s a sample score report of two sections that would provide you with a better understanding of the result:
How Long Does It Take To Get PPR Scores Back?
After taking the PPR exam, you may anticipate receiving your test results by email the day after the TExES score report date. On the report date for your exam, scores will also be accessible on your Pearson account starting at 10:00 p.m. Central time. You may anticipate receiving your test results for pure selected-response (multiple choice) examinations in 7–10 business days.
On the Texas Educator Certification Examination Program website, there is a score report date feature where you may enter your testing date and view the anticipated timeframe in which your scores will become accessible. If you took a test that was recently designed or changed, or if there were issues with your registration or payment, your results might be delayed.
If you don’t pay for your exam or don’t have permission to take it, your results would not be generated. You have the option to report your test results or cancel the PPR test at the end. Your TExES results will not be recorded, and it won’t count as a testing attempt if you decide to cancel. Also, you won’t receive any refunds.
Where To See Your Score
The TExES scores can be delivered to your email on the score report date when you register for the test. On the report date for your exam, starting at 10:00 p.m. Central time, your scores will also be accessible on your Pearson account. Your outcomes are instantly submitted to your TEA certification profile and, if necessary, your program or agency. You will still need to finish the certification application procedure in order to get certified, even though your test results will be accessible.
iPREP: Concise. Focused. What you need.
Sign up
Immediate access
Practice
Online self-paced
Pass
Ace that Test!
FAQs
The TExES PPR test is an exam designed to assess the pedagogical and professional knowledge and skills of individuals seeking certification as educators in Texas. It evaluates candidates’ understanding of teaching techniques, classroom management, ethical and legal responsibilities, and professional development.
The TExES PPR practice test is an invaluable resource for candidates preparing to take the actual exam. It allows you to familiarize yourself with the test format, content, and level of difficulty. By taking the practice test, you can identify areas of strength and weakness and accordingly tailor your study plan.
How can I access the PPR practice test?
The official TExES website offers a variety of resources, including practice tests, for candidates preparing for certification exams. You can access the TExES PPR practice test through the official website or by exploring other reputable online platforms that provide study materials for the TExES exams.
The practice test covers various topics related to pedagogy and professional responsibilities. It includes questions on instructional design and delivery, assessment and evaluation, learning environments, diversity and inclusivity, and professional development. It also assesses candidates’ understanding of legal and ethical responsibilities in the education field.
The duration of the practice test may vary, but it typically consists of a predetermined number of multiple-choice questions. The actual test is four hours long, but the practice test may be shorter or longer depending on the platform or resource you are using.
The TExES PPR practice test is primarily focused on assessing your pedagogical and professional knowledge, so it does not require the use of calculators or any other aids. It aims to evaluate your understanding of teaching concepts, strategies, and ethical considerations.
Yes, there are numerous study materials available to help you prepare for the TExES PPR practice test. These resources include study guides, textbooks, online courses, and practice tests. The official TExES website provides a comprehensive list of recommended study materials that you can access to enhance your preparation.
PPR Exam Test Tips
Here are some valuable hints for test day, as you will likely spend the majority of your time studying and getting ready for the exam:
- Spend quality time in bed so that you may wake up rested on test day.
- Be careful to arrive at the testing location at least 30 minutes early and to bring two kinds of legal identification.
- You will need the energy, so eat before the test!
- Avoid spending unnecessary time demanding answers by skipping them and coming back to them at the end. This will save up time that you can use to answer other questions.
- Before choosing the correct response, thoroughly read the question and possible replies. There are phrases like “which of the following does” and “which of the following does not” that you will come across. If you answer the question quickly, you can choose the wrong response.
- Do not let the lack of a pattern in the responses affect the one you choose.
- Consider your pace and the passing of time.
- Do not become anxious about your exam performance or frustrated when encountering challenging questions. Do not let your score distract you from answering the questions.
- If unsure about the correct response, try eliminating as many viable options as possible. If all else fails, guess. No points are deducted for inaccurate answers, and unanswered questions are not worth any points.
- Stay at ease and relaxed; you got this!
Here’s a tip from a test-taker:
“Keep working through the practice tests. It’s not why your answers are correct, but why your answers were wrong.
Hint: Especially for PPR, whatever the scenario, pretend that it’s taking place in Disneyland ISD. Life is perfect there.”
Source: Reddit/dkstr419
Administration
Test Administrators: The Educational Testing Service (ETS) administers the PPR computer-adaptive test for the Texas Education Agency (TEA). The TExES examinations, necessary for teacher certification in Texas, are created and administered by ETS, a nonprofit organization.
Test Schedule: Applicants will be provided with 170 days after paying to schedule an exam date, and if they fail to do so, their registration will be canceled, and no refund of their payment will be issued.
Test Format: Multiple choice and computer-based
Test Materials: Apart from a valid ID proof, no other material would be allowed in the testing facility.
Cost: The registration fee is $116, which can be paid using a debit or check card with the VISA or MasterCard logo, a VISA or MasterCard credit card, or both.
Retake Policy: You can take the exam 5 times in total. However, you must wait at least 45 days from your initial attempt before applying for a retake.
Test Provider
The TExES Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities (PPR) EC-12 (160) exam is administered by the Texas Educator Certification Examination Program (Texas Education Agency – TEA) and Pearson. Pearson is a leading global educational publishing and assessment company that collaborates with TEA to develop and administer the TExES exams.
Information Sources
- TEA – Texas Education Agency
- Texas Educator Certification Examination Program
- Texas Teachers for Tomorrow
Disclaimer – Every study guide and tutoring material on iPrep is accurate and was written only for the purpose of providing assistance. Iprep is not affiliated with the TExES Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities (PPR) EC-12 (160) exam, Texas Educator Certification Examination Program (Texas Education Agency – TEA), Pearson, Educational Testing Service (ETS) or any other brands or businesses mentioned in the content above.
Free PPR practice test: Get to know what the PPR Test will be like by practicing with these sample questions:
Domain 1 Sample Questions:
Question 1 to 4
To ensure that a final project accurately evaluates what third-grade students have comprehended from a unit on local ecosystems, a teacher should incorporate which of the following in the assessment process?
- Opportunities for students to rank their work against that of their classmates.
- Resources for students to develop goal-setting strategies for future units.
- A sneak peek at ideas and resources related to the forthcoming unit on climate change.
- A range of methods for students to demonstrate their comprehension.
The correct answer is (D) A range of methods for students to demonstrate their comprehension.
Explanation
Different students have different learning styles and may express their understanding in a variety of ways. By offering multiple methods for students to demonstrate their understanding (such as written explanations, drawings, oral presentations, or models), the teacher ensures a more equitable and accurate assessment of what each student has learned.
Answer (A), opportunities for students to rank their work against that of their classmates, can lead to unhealthy competition and self-esteem issues, particularly at this age. It also does not guarantee an accurate measure of what students have learned.
Answer (B), providing resources for students to develop goal-setting strategies for future units, while potentially beneficial for long-term learning, does not directly help in accurately assessing the learning outcome of the current unit.
Answer (C), a sneak peek at ideas and resources related to the forthcoming unit on climate change, while possibly engaging and beneficial for transition into the new unit, is not directly relevant to assessing what students have learned from the current unit on local ecosystems.
Question 2 to 4
A second-grade class will be utilizing learning centers. The main aim of the centers is to cultivate an environment where students choose activities to engage with, finish their tasks, and share their gained knowledge. Despite the teacher’s detailed planning of the tasks at the centers, some students remain uncertain about what to do. Which of the following actions would best assist the students in understanding how to use the learning centers to foster independent learning?
- Displaying the criteria for student performance for the center’s activities.
- Enlisting student volunteers to demonstrate how to work in the centers.
- Detailing expected student conduct for working in the centers.
- Creating a rubric for students to use in evaluating the quality of their tasks.
The correct answer is (B) Enlisting student volunteers to demonstrate how to work in the centers..
Explanation
Having student volunteers demonstrate how to use the learning centers effectively offers a practical, visual demonstration that can enhance understanding. Role-playing can make the process clearer, particularly for younger students who often benefit from concrete, visual learning experiences.
Answer (A), displaying the criteria for student performance for the center’s activities, would be helpful but might not provide the hands-on and visual support needed to clarify the procedures.
Answer (C), detailing expected student conduct for working in the centers, is an important part of classroom management, but it doesn’t provide the practical instruction the students need to understand how to use the learning centers effectively.
Answer (D), creating a rubric for students to use in evaluating the quality of their tasks, can be useful for assessment but doesn’t directly address how students should use the learning centers.
Question 3 of 4
Ms. Johnson evaluates the following student data from a diagnostic math benchmark test. She notes the number of correct responses in each category and plans to hold individual meetings with each student to set their individual math goals.
Math Benchmark Data
| Calculation (20 items) | Fractions (15 items) | Geometry (10 items) | Problem Solving (20 items) | TOTAL (65 Items) | |
| Jessica | 18 | 13 | 8 | 15 | 54 |
| Carlos | 16 | 12 | 7 | 14 | 49 |
| Tara | 17 | 15 | 9 | 18 | 59 |
| Sam | 14 | 11 | 6 | 13 | 44 |
| Daisy | 18 | 14 | 8 | 17 | 57 |
- their overall performance on the math benchmark compared to other subjects.
- their performance on the same math benchmark from the previous year.
- the performance of other students in the class on the math benchmark.
- their individual strengths and weaknesses as highlighted in the benchmark data.
The correct answer is (D) their individual strengths and weaknesses as highlighted in the benchmark data.
Explanation
The correct answer is D because individual strengths and weaknesses highlighted in the benchmark data would be the most beneficial in setting personal goals. This data can help students identify areas where they can improve and those where they excel, making it more specific and personally applicable.
Option A is incorrect because comparing performance across subjects may not provide a clear direction for setting goals within a specific area, like math.
Option B is incorrect as it might not be beneficial for students to only compare their performance to the previous year, especially if they have already made significant progress or if the content of the benchmark has changed.
Option C is incorrect as it encourages comparison with others, which might not be beneficial or fair as each student’s skills and pace of learning can differ. The primary focus should be on individual progress and not on competition with others.
Question 4 (for the same table) to 4
The statistical measurement that will best help Ms. Johnson identify the needs of her entire class is the
- mode of the total number of items answered correctly.
- median of the total items answered correctly as a percentage
- mean of the percentage correct for each category.
- range of the category totals for the class.
The correct answer is (C) mean of the percentage correct for each category.
Explanation
The correct answer is C because by calculating the mean (average) of the percentage correct for each category, Ms. Johnson can determine how well the class as a whole is understanding different areas of the subject. If the mean percentage is low in a particular category, it may indicate that the class is struggling in that area, and she may need to adjust her instruction or provide more practice in that category.
Option A, the mode of the total number of items answered correctly, would not be as useful because it only identifies the score that appears most frequently, which may not be representative of the class’s overall performance.
Option B, the median of the total items answered correctly as a percentage, provides the middle score when all scores are listed in numerical order. While this gives some insight into class performance, it doesn’t provide a detailed breakdown by category like option C does.
Option D, the range of the category totals for the class, gives the difference between the highest and lowest scores. While this shows the spread of scores in the class, it doesn’t give an accurate reflection of the overall performance or needs of the class.
Domain 2 Sample Questions:
Question 1 to 3
At the start of the academic year, a primary school teacher intends to establish clear classroom rules. To most effectively accomplish this goal, the teacher should have students:
- Role-play the classroom rules.
- Design a personalized version of the classroom rules.
- Recite the classroom rules by heart.
- Write an essay on the significance of classroom rules.
The correct answer is (A) Role-play the classroom rules.
Explanation:
Having students role-play the classroom rules will help them understand and internalize these rules in a practical manner. This approach promotes active learning and enables students to understand the purpose and relevance of the rules in a real-world context.
Option (B), designing a personalized version of the classroom rules, could lead to confusion or inconsistency in understanding and implementing the rules among different students.
Option (C), reciting the classroom rules by heart, might not ensure a deep understanding of the rules or why they are important. Moreover, it focuses on rote memorization rather than practical application.
Option (D), writing an essay on the significance of classroom rules, might be too complex a task for younger elementary students. Furthermore, this approach emphasizes theoretical understanding over practical application of the rules.
Question 2 to 3
An instructor provides an art project to the students and meticulously explains the steps for gathering the required materials and storing them back in their designated locations once the project is completed. The main reason for elucidating these steps is to
- set a benchmark for the students’ performance.
- enhance students’ problem-solving abilities.
- foster students’ skills in resource management.
- facilitate interaction among students.
The correct answer is (C) foster students’ skills in resource management.
Explanation:
The correct answer is C, as the main purpose of the teacher outlining the steps for gathering and storing supplies is to promote students’ organizational and resource management skills. By understanding and following these steps, students can learn to be more systematic, disciplined, and responsible, which are crucial skills for personal and academic success.
Option A, setting a benchmark for students’ performance, while important, is not the primary purpose of these instructions. High expectations typically refer to academic or behavioral standards, not procedural ones.
Option B, enhancing students’ problem-solving abilities, may be a side effect of many classroom activities, but it’s not the main goal in this instance. The task doesn’t inherently involve problem-solving.
Option D, facilitating interaction among students, is also not the main objective here. While group activities and shared resources can promote socialization, the primary goal of the described process is the individual management of resources.
Question 3 to 3
A seventh-grade geography teacher is planning a month-long project where students will simulate the workings of different governments in groups. When the teacher is setting up the groups, which of the following strategies is most likely to encourage effective teamwork among group members?
- Allowing students total freedom in selecting their groups and the size of each group.
- Informing each group that individual contributions will be collectively graded.
- Requiring each group to devise a teamwork strategy, specifying roles, which they then discuss with the teacher.
- Minimizing teacher intervention unless explicitly requested by the group.
The correct answer is (C) Requiring each group to devise a teamwork strategy, specifying roles, which they then discuss with the teacher..
Explanation:
The correct answer is C. When students are asked to devise a teamwork strategy and clarify roles, they are encouraged to communicate and deliberate on the distribution of tasks and responsibilities. This promotes accountability, organization, and a shared understanding of what is expected of each member, which is crucial for effective collaboration. Reviewing this strategy with the teacher also offers a chance for guidance and feedback.
Option A, while giving students autonomy, might not guarantee balanced or effective groups. Some students might gravitate towards friends rather than considering the skills needed for the project.
Option B, while it might encourage some shared responsibility, it might also lead to unequal contribution, as some members might rely on others to achieve a good grade.
Option D may leave some groups struggling without necessary guidance. Regular check-ins, even if not explicitly requested, help ensure that groups stay on track and tackle potential issues early on.
Domain 3 Sample Questions:
Question 1 to 4
Middle school students utilize online platforms to investigate comprehensive inquiries about global cultures. The primary advantage for students to use technology rather than hardcopy resources for this type of research is that technology enables students to:
- Help each other in understanding complex cultural terminologies.
- Utilize more authoritative sources than hardcopy texts can provide.
- Access the most recent global cultural information available.
- Learn about different cultures in age-appropriate language.
The correct answer is (C) Access the most recent global cultural information available.
Explanation:
The use of technology, particularly the internet, allows for real-time updates and provides access to the most current information available. This is especially important when researching global cultures as events, policies, and societal changes can significantly alter cultural landscapes.
Answer (A), helping each other understand complex cultural terminologies, is beneficial but is not the primary advantage of using technology. It is also possible to help each other understand complex terms when using printed resources.
Answer (B), utilizing more authoritative sources than hardcopy texts can provide, is not always accurate. The reliability or authority of a source is not determined by its medium (print or digital) but by its content and origin.
Answer (D), learning about different cultures in age-appropriate language, is a potential benefit of certain online resources that adjust language level for different age groups, but it’s not the main reason to choose technology over print for research. Both printed and online resources can offer age-appropriate content.
Question 2 to 4
A teacher is planning a lesson involving the use of online resources at school. However, some students don’t have parental consent to access the internet. Which of the following should the teacher do to best accommodate these students?
- Load the required online pages for the students so they can follow the lesson with their peers.
- Allow the students to enhance their computer skills by exploring other computer software without internet access.
- Encourage the parents to reconsider their stance and allow their children to use the internet at school.
- Organize a comparable offline activity for the students that includes the same content being taught to the rest of the class.
The correct answer is (D) Organize a comparable offline activity for the students that includes the same content being taught to the rest of the class.
Explanation:
Providing an alternative activity that covers the same material ensures that all students can participate and learn the same content, even if they can’t access the internet. This action respects parental decisions while maintaining educational equity.
Answer (A), loading the required online pages for the students, might infringe on parental preferences and could potentially violate school policy.
Answer (B), allowing the students to enhance their computer skills without internet access, may be valuable but doesn’t ensure they’ll learn the same material as the rest of the class.
Answer (C), encouraging the parents to reconsider their stance, could come across as disrespectful of parental decisions and might not solve the immediate need for an alternate learning activity.
Question 3 to 4
A kindergarten teacher is initiating a new lesson on plants. To introduce this topic, which of the following teaching methods most effectively supports learning through hands-on exploration?
- Supplying students with an assortment of plant samples for tactile exploration followed by a discussion of their observations.
- Reading a children’s story about plants and conversing about students’ pre-existing knowledge regarding plants.
- Demonstrating a brief skit using props, illustrating the process of photosynthesis.
- Displaying an illustrated chart showcasing different plant species and subsequently discussing the chart with the pupils.
The correct answer is (A) Supplying students with an assortment of plant samples for tactile exploration followed by a discussion of their observations.
Explanation:
The correct answer is A. Giving students an assortment of plant samples enables them to actively engage and learn through tactile and sensory experiences. Discussing their observations further cements their understanding.
Option B, while useful in tapping into students’ prior knowledge, doesn’t necessarily involve active play or hands-on exploration.
Option C, although interactive and likely entertaining, may introduce a concept (photosynthesis) that’s too advanced for kindergarten students and doesn’t encourage hands-on learning.
Option D is more of a passive learning experience. While discussing the illustrated chart can be informative, it doesn’t provide the same tactile experience as option A.
Question 4 to 4
Use the conversation between a teacher and a student to answer the subsequent question.
- Ms. Archer: Can you tell me the volume of the three boxes displayed, Kevin?
- Kevin: They all hold the same volume. It’s 24.
- Ms. Archer: How about the surface areas of the three boxes?
- Kevin: Each one is different.
- Ms. Archer: Why do you think that’s the case, Kevin?
The main objective of Ms. Archer’s line of questioning is to encourage Kevin’s ability to
- formulate hypotheses
- share opinions with classmates.
- pinpoint a misconception.
- deepen his understanding.
The correct answer is (D) deepen his understanding.
Explanation:
The correct answer is D. Ms. Archer’s questions are designed to get Kevin to think critically about the relationships between volume and surface area. By asking Kevin to observe and then ponder on the differences in surface area while having the same volume, she’s pushing him to delve deeper into the concepts, thereby deepening his understanding.
Option A might not be the primary intent as the questions are not focusing on Kevin’s ability to work without guidance but more on understanding the relationship between volume and surface area.
Option B is incorrect because the conversation doesn’t emphasize interaction with peers.
Option C is not the main goal, as the questions are not set up to identify a misconception but to foster a deeper grasp of the topic.
Domain 4 Sample Questions:
Question 1 to 4
In Texas, routine teacher assessments are carried out chiefly to identify:
- a teacher’s eligibility for tenure.
- possible areas for a teacher’s professional improvement.
- the sort of insurance package a teacher will be granted.
- whether a teacher possesses qualities for mentorship roles.
The correct answer is (B) possible areas for a teacher’s professional improvement.
Explanation:
The principal objective of teacher evaluations in Texas is to help identify strengths and weaknesses in a teacher’s performance, which can guide the creation of a personalized professional development plan. This process fosters continuous growth and improvement in teaching quality.
Answer (A), a teacher’s eligibility for tenure, while potentially influenced by performance assessments, is not the primary purpose of these evaluations. The decision for granting tenure typically involves multiple factors, not just annual evaluations.
Answer (C), the sort of insurance package a teacher will be granted, is typically determined by school district policies or union contracts, and not directly linked to the outcomes of a teacher’s annual performance appraisal.
Answer (D), whether a teacher possesses qualities for mentorship roles, may be a secondary benefit of the appraisal process but is not its main goal. While leadership or mentorship potential could be revealed through evaluations, the primary focus is on enhancing teaching effectiveness and identifying areas for professional growth.
Question 2 to 4
A teacher is keen on acquiring more knowledge about addressing the requirements of students with special needs. The school district where the teacher is employed does not presently provide any additional training on the subject. Which of the following will most effectively cater to the teacher’s professional development necessities?
- The state board of education
- The principal’s office
- The school district’s administrative council
- The closest regional special education resource center
The correct answer is (D) The closest regional special education resource center.
Explanation:
Regional education service centers often provide professional development opportunities, resources, and training on a variety of topics, including special education. These centers have specialists who can provide specific strategies and methods to support students with special needs.
Answer (A), the state board of education, while it does set policies and guidelines, typically does not directly provide professional development training to individual teachers.
Answer (B), the principal’s office, although potentially a source of guidance and direction, may not offer the specific professional development resources the teacher is looking for, especially if the district itself isn’t currently offering any new classes on the topic.
Answer (C), the school district’s administrative council, is more involved with policymaking and administrative decisions than providing direct professional development resources to teachers.
Question 3 to 4
After a detailed discussion in a parent-teacher meeting about Alex, both the teacher and the parents decide on a method to track his progress on his behavior agreement, which was designed to encourage good behavior in school. Through committing to and following this approach, the teacher and the parents showcase their belief that
- behavior agreements are paramount in gaining family endorsement for a student.
- consistent communication is a fundamental element of an effective behavior agreement.
- deliberate family participation in a student’s academic journey can encourage good behavior.
- students being actively engaged in setting behavioral targets enhances the achievement of those targets.
The correct answer is (C) deliberate family participation in a student’s academic journey can encourage good behavior.
Explanation:
The correct answer is C. The decision to monitor and track Alex’s behavior in school indicates an acknowledgment by both the teacher and parents that when families are actively and purposely involved in their child’s educational journey, it can lead to better behaviors at school.
Option A is not accurate as the scenario does not imply that behavior agreements are the “most effective” means, only that they are a tool being used.
Option B might seem correct, but the question doesn’t explicitly state that the communication has to be on a “daily basis.”
Option D is not supported by the provided information since the focus of the scenario is on the involvement of the teacher and parents, not on the active participation of the student in setting goals.
Question 4 to 4
Mrs. Ramos, a sixth-grade biology teacher, discusses the importance of laboratory safety protocols with her students. To kick off the project, Mrs. Ramos showcases exemplary posters made by students in prior years, initiating a discussion about the elements that make these posters effective. She then instructs the students to design their posters to display their comprehension of safe laboratory procedures. Once the posters are finalized, Mrs. Ramos plans to exhibit them in the classroom. To best align with national and state ethical and legal standards, before displaying the students’ work, Mrs. Ramos should
- secure students’ agreement to display the posters.
- substitute students’ names with unique codes on the posters.
- acquire parental consent to exhibit the posters.
- exclude any grade or score from the posters.
The correct answer is (D) exclude any grade or score from the posters..
Explanation:
The correct answer is D. According to the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), it’s a violation to publicly display students’ grades without consent. By ensuring that students’ grades are omitted from the posters, Mrs. Ramos is aligning her actions with national and state ethical and legal guidelines.
Option A might seem like a plausible choice, but the primary concern isn’t about displaying the poster itself but rather any potentially sensitive information on it.
Option B, although it respects anonymity, doesn’t directly address the specific concern of displaying grades or scores.
Option C is not the most suitable choice in this context as it’s not typically required to obtain parental consent for displaying student work in a classroom, but it is essential to ensure that any displayed work does not violate students’ privacy rights by including sensitive academic information.
Well done!
You have completed the Sample Questions section.
The complete iPREP course includes full test simulations with detailed explanations and study guides.
‘…TESTS THAT ACTUALLY HELP’

In the first 30 minutes of use I have learned so much more than skipping along the internet looking for free content. Don’t waste you time, pay and get tests that actually help.
Richard Rodgers
January 28, 2020 at 7:49 PM