iPREP is a trusted test‑prep provider offering a full Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test II (BMCT-II) prep course, and on this page you can access free sample questions with full explanations and video walkthroughs.
You’ll get:
- Free real‑style Bennett Mechanical questions
- Instant right/wrong feedback
- Step‑by‑step written solutions
- Short video explanations for every answer
Test Breakdown with Sample Questions
Each Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test is unique, as the test is generated from a bank of questions. This ensures that each BMCT test is equal in terms of difficulty, while preventing people from getting a copy of the test. As this is a mechanical exam, be prepared for questions dealing with gears and belt drives, gravity and velocity, hydraulics, pulleys and levers, structures, planes and slopes, and others.
Twelve BMCT Question Categories
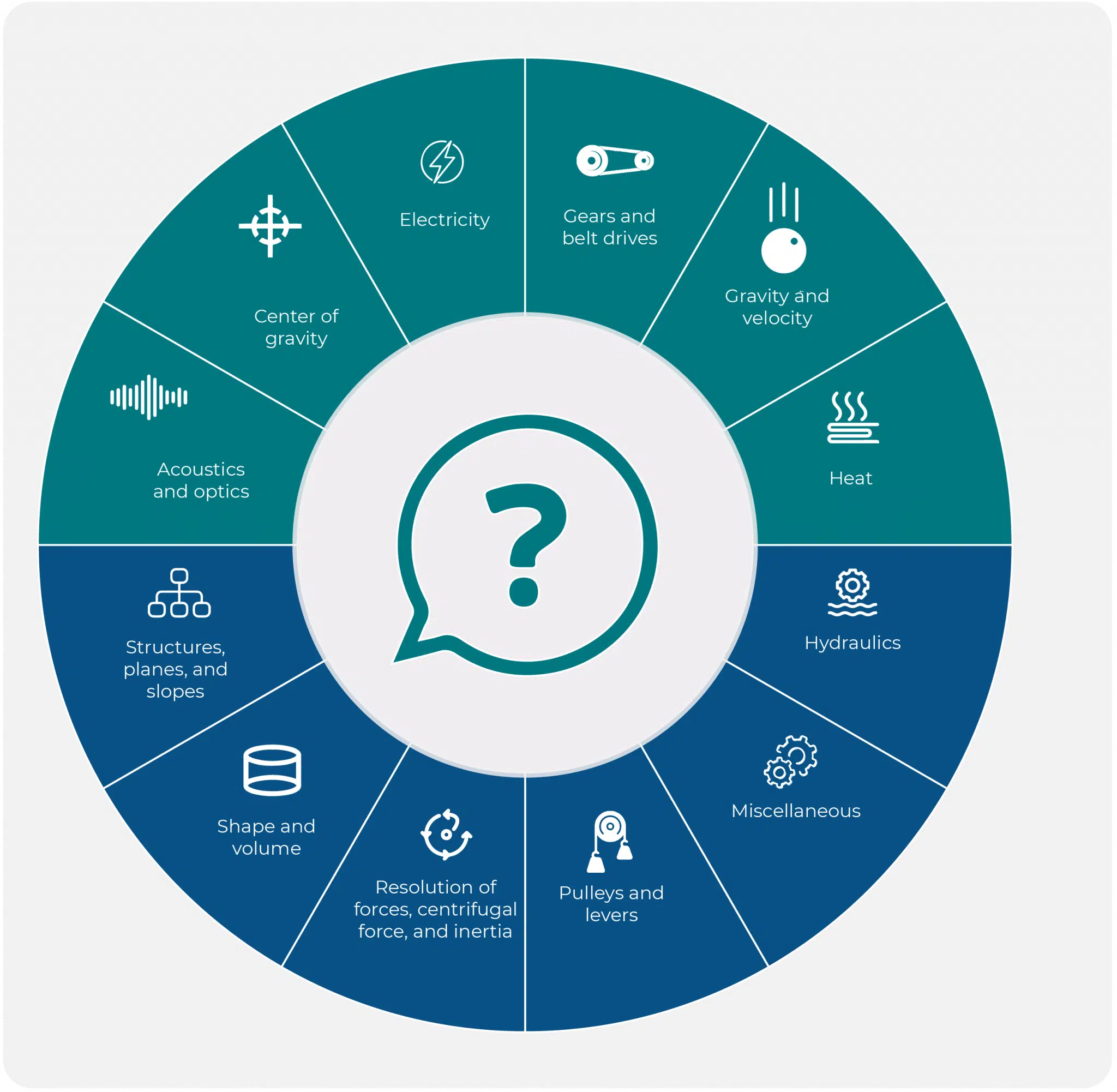
The BMCT II contains 12 categories of mechanical questions, distributed according to the following table:
| Category | No. of questions |
|---|---|
| Acoustics and optics | 3 |
| Center of gravity | 3 |
| Electricity | 3 |
| Gears and belt drives | 5 |
| Gravity and velocity | 4 |
| Heat | 3 |
| Hydraulics | 6 |
| Miscellaneous | 6 |
| Pulleys and levers | 7 |
| Resolution of forces, centrifugal force, and inertia | 6 |
| Shape and volume | 3 |
| Structures, planes, and slopes | 6 |
| Total number of questions | 55 |
Free BMCT Sample Questions
Here are some free sample questions for the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test, one question for each of the BMCT-II question categories.
Acoustics and Optics
These questions assess basic physical properties of acoustics and optics such the speed of sound/light, the Doppler Effect, light reflections, and more.
Acoustics and Optics Sample Question
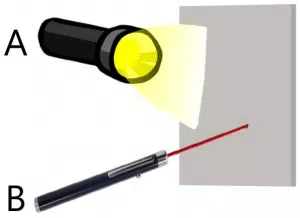
The light of which device will reach the screen faster?
(If at the same time, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is C.
Light is an electromagnetic wave, having a constant speed for a given medium. From the figure, it can be seen that two light sources are pointed at a screen, a flashlight and a laser pointer.
In the case of the flashlight, the light of varying frequencies and wavelengths is being emitted from the filament of the bulb, in all directions. However, the emitted light is an electromagnetic wave as well and its speed will remain constant according to the equation:
speed of light (c) = frequency (f) * wavelength (λ)
In the case of a laser, directed light rays of only a single frequency and wavelength are being emitted. However, the speed of light remains the same since the emitted rays are electromagnetic waves too, which propagate through the same medium. Therefore both lights will reach the screen at the same time.
Center of Gravity
These questions examine the concept of physical balance, and how the center of gravity may influence the effort that should be exerted to perform an action, the movement of an object, and more.
Center of Gravity Sample Question
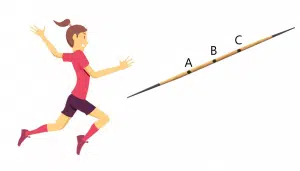
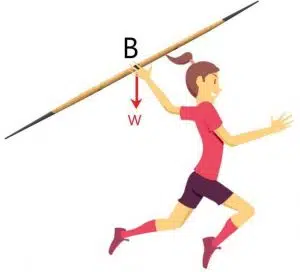
Which grip position will allow the thrower to get the javelin farther?
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is B.
The given problem provides three possible positions at which the javelin can be held while thrown. It is, of course, important to hold the javelin at the point where the least amount of effort is required. This ensures all the effort is geared towards throwing the javelin rather than simply holding it.
It can be seen that point B lies in the middle of the javelin, which is the position of the center of mass. When an object is held at its center of mass, no moment is required to keep it balanced. Hence the best position to hold the javelin is at its center of mass, which is the position B.
Electricity
These questions assess your basic knowledge of electricity, with an emphasis on conduction and basic electric circuits.
Electric Circuits Sample Question
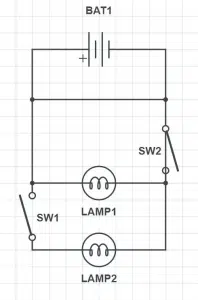
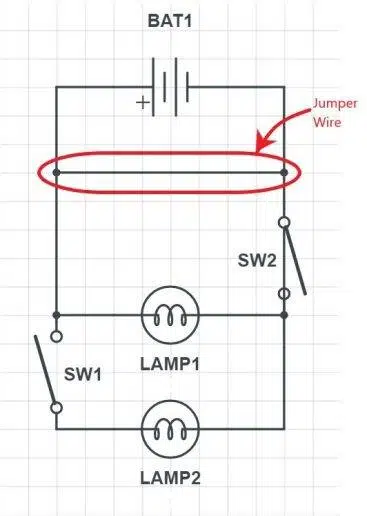
In the current structure, switch 1 is on and switch 2 is off. Which lamp will light up?
- Lamp 1
- Lamp 2
- Both/neither
The correct answer is C – neither.
It can be seen from the structure that the given circuit is short-circuited by a jumper wire connecting the two terminals, highlighted in the figure below. A short circuit occurs when two nodes having a finite potential difference are connected to each other without having any resistance between them.
According to Ohms’ Law: Current (I) = Potential Difference (V) / Resistance (R)
If resistance is near zero, then the amount of current flow will be very large. Since current always takes the path of least resistance, it will move through the jumper wire and will not pass through the bulbs. In this case, we do not need to consider the configuration of the switches.
Gears and Belt Drives
These questions will present various scenarios involving several rotating gears that are either meshed together or connected with a belt drive. You will be required to answer questions regarding speed.
Gears Sample Question

Which mechanism would move the chain more slowly?
(If there is no difference, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is A.
You know that the tangential speed of meshed gears is the same. Also, the rotational speed and radius of the gear are inversely related to constant tangential speed. In mechanism A, the driving gear (on the left) meshes with a larger gear. The smaller gear which moves the chain is connected on the same shaft as the larger gear, which means that the rotational speed of the smaller gear is equal to that of the larger gear.
However, in mechanism B, the driving gear directly meshes with the small gear, which drives the chain. This means that the smaller gear will rotate faster than the larger gear in mechanism A, which implies that the chain will move faster in mechanism B.
Gravity and Velocity
The scenarios in this section will present various scenarios that involve moving objects—either vertical moving objects (gravity), horizontally moving objects (velocity), or a combination of these forces (e.g. trajectory of a thrown object).
Gravity and Velocity Sample Question

Which gunman’s bullet will strike the ground first?
(If at the same time, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is B.
From the given figure, gunman A is holding his gun upwards at an angle whereas gunman B is holding the gun completely horizontally. If you extrapolate the trajectory of the bullet in the vertical direction (see the figure below), you can conclude that the bullet in case A will first move upwards due to its initial velocity. Then after some time, it will start moving downwards due to gravity and come to the level of its initial height, and only then fall down to the ground.
In the case of bullet B, it will not go upwards since the initial velocity is horizontal; instead, it will move directly downwards due to gravity.
Since only the downward acceleration is acting on the body (the gravitational acceleration “g”), bullet A will start moving downwards after reaching the highest point, while bullet B will move downwards from the beginning.
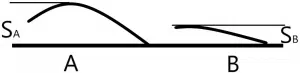
Heat
These questions will examine the effect of changing temperature (heat and cold) over the physical properties of materials—for example—the behavior of hotter and cooler gas. They may also examine different scenarios that create heat (e.g. through friction).
Heat Sample Question

Which plastic bottle is more likely to melt upon touching the fire?
(If equally likely, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is A.
When the bottle is placed near the fire, heat conduction will start from the fire to the bottle. This heat will increase the temperature of the bottle. When the temperature of the bottle reaches the melting point of plastic, it will melt. Now, the time taken for the temperature to reach the melting point is the main consideration of this problem. When the bottle surface heats up due to the fire, a temperature difference will be created between the water contained within the bottle and the bottle surface. Since heat travels from a hot body to a cold body, the bottle will transfer the heat to water until it reaches the same temperature as the bottle.
Since the volume of water in bottle B is greater, it will take longer to heat up. Bottle A will heat up to the melting point of plastic faster and therefore it is more likely to melt.
Hydraulics
Various aspects of hydraulics will be examined through these scenarios including the influence of the volume, the altitude, and the diameter of a vessel/pipe on water pressure. It may also look into the compressibility of fluids and the influence of water pressure over other materials.
Hydraulics Sample Question
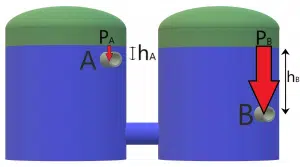
Two water jets are ejected from tank-pipes A and B. Which jet will reach farther?
(If equal, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is B.
You know that the hydrostatic pressure inside a tank filled with liquid is defined as: P=ρgh, where ρ is the density of the liquid, g is the gravitational acceleration, and h is the depth of the point where pressure is being measured from the liquid level.
Now, in the case of pipe A, the pressure exerting at that point will be due to the water head (hA) above point A, which is relatively low, as can be seen in the image. For point B, the pressure will be due to pressure head (hB) which is greater. Since hB>hA, the water jet B will shoot farther.
Did you know? – The Torricelli Theorem gives the speed of a water jet as v = √2gh
Miscellaneous
Additional every-day scenarios that do not necessarily fall onto any of the categories mentioned or combine various mechanical phenomena.
Springs Sample Question
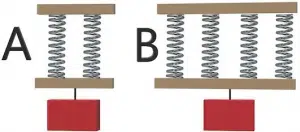
The same load is being hung from each construct, made up of springs with the same length and stiffness. In which construct will the spring extensions be longer?
(If equal, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is A.
In both constructs, springs are placed in parallel. An in-parallel arrangement of springs increases their stiffness since the force extending the spring has to work against multiple spring forces. Therefore, the effective spring constant of the setup is increased.
If the spring constant of each given spring is “k,” then the equivalent spring constant is given as
kA = 2k and kB = 4k
Extension in the spring is given by Hooke’s law as:
Force (F) = Spring constant (k) * Extension (x)
For constant force, the extension of spring is inversely related to the spring constant. The extension in construct A will be double the extension of construct B since its spring constant is half that of B.
Pulleys and Levers
These questions will usually compare two different measures of the same characteristic of the simple machine’s pulleys and levers, especially through the prism of the mechanical advantage they provide. For example, pulley questions will compare the number of ropes and pulleys in a pulley system and their effect on the force needed to lift the weight; lever questions will compare properties such as the length of the arms and the position of the weight on the force required to lift the weight.
Pulleys Sample Question
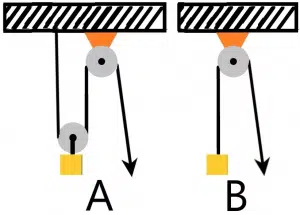
Which pulley mechanism reduces the effort of lifting a similar weight?
(If both reduce the effort, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is A.
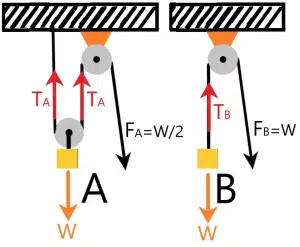
In order to find the force required to lift the load, you need to determine the tension (W) in the string for both A and B—this can be seen in the image below.
Foe mechanism A, W =TA + TA; therefore TA = W/2
Foe mechanism A, W = TB, or TB = W
Now, the pulling force required to lift will be equal to the tension in the string that is holding the load. Tension is equally distributed between all pieces of the string pulling the load. Tension will decrease if you increase the number of strings pulling the load. In the given case, the tension in the string is W/2 for mechanism A and W for mechanism B. Hence, mechanism A reduces the required effort by half.
Resolution of Forces, Centrifugal Force, and Inertia
In these questions, scenarios from various fields may be presented. In each of these, the focus will be on force moment, or the interaction between two forces.
Forces Sample Question

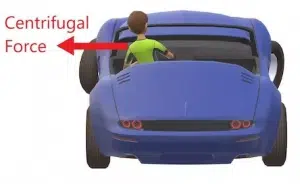
While taking a right turn, which driver position is more likely to happen?
(If equal, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is B.
The car is taking a right turn, which means that it has a lateral component of velocity (v) in the right direction. This component governs the revolving motion of the car. When a body revolves around an axis, it faces centripetal force which is directed towards that axis. However, due to inertia, an opposite force acts on the body which is directed away from the central axis, known as centrifugal force. Because of this force, an object moving along a circular path tends to move outside the circle.
In the given case, the driver will also be pushed outside the circle by centrifugal force, as shown by position B.
Shape and Volume
These questions are not supposed to assess your math skills but your understanding of geometrical properties and the relationship between different shapes and volume.
Volume Sample Question

Object A is made of material twice as dense as object B. Which object is more likely to float in water?
(If same likelihood, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is B.
The upward force of water acting against the weight of the bodies is known as buoyancy. It is known that the buoyant force does not depend on weight but rather on the density of an object. In our case, the density of object A is twice that of object B, therefore, object B is more likely to float.
This can be mathematically expressed as:
Buoyant Force B = density of water (ρW) × displaced volume of water (VW) × gravitational acc.(g)
This force acts against the weight of the object, which is defined as:
Weight (W) = mass(m) × gravitational acc.(g), where
mass (m) = density of an object(ρ) × immersed volume of the object (V)
Structures, Planes, and Slopes
These questions may compare different structures for their durability, or for the force required to climb/overpass them.
Planes and Slopes Sample Question

Which slide will be faster?
(If impossible to tell, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is A.
The slide is an example of an inclined plane, in which the component of gravity acting along the incline is responsible for pulling the person downwards. We know that a helix can be converted into an inclined plane, as shown in the figure below. The length of the incline increases if it is in the shape of a helix, as compared to a straight incline. The speed of an object moving down an inclined plane increases as the angle of the incline increases due to an increase in the component of gravity acting along the incline. However, if the angle of the helix and the straight incline are the same, then the speed of the object will be equal.
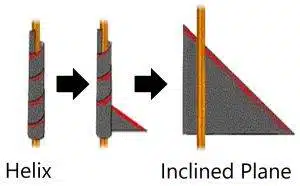
In the above problem, the path of slide B is longer than that of A and the angle of inclination seems the same, however, if the helix is converted to a straight incline, the angle becomes more moderate. Therefore, the force pulling the person downwards will be smaller for the helix. From the 2nd equation of motion, we can determine that slide A will take less time compared to slide B, hence it will be faster.
Did you know?
The Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test contains 12 categories of mechanical questions; the most common are: (1) pulleys, levers & gears, (2) hydraulics, (3) structures, planes, and slopes, and (4) gravity and other forces. You must score 80% or higher to be chosen for a job. To do well on the test, you need to display mechanical comprehension and understand the key principles underlying simple machines and basic physical concepts.
BMCT Preparation Strategies
1. Get Into “Test Mode” State of Mind
Mechanics is science, and all the answers can be calculated using the data provided. However, the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test does not require you to calculate the correct answer; you only need to understand the mechanical principle underlying the question and provide an answer based on that. Therefore, remember these rules of thumb for test day:
- Each BMCT question focuses on one mechanical principle—begin by identifying the mechanical principle and then determine how it may affect the scenario.
- Environmental elements should be ignored—you should completely ignore characteristics of the scenario, unless they are the main element. For example, do not consider friction unless the question focuses on that.
2. Refresh Your Knowledge of Mechanical Concepts
Your chances of success on the Bennett test rely not only on your logical thinking but also on your (surprise, surprise…) mechanical comprehension. On the one hand, you do not need to possess any professional knowledge in mechanics or memorize mathematical formulas. On the other hand, you should aim for an absolute grasp of some concepts. Try to find a study guide that covers:
- Basic mechanical concepts such as gravity, velocity, friction, potential energy (e.g. springs), hydraulic pressure, and mechanical advantage
- Simple machines and the mechanical advantage they provide—lever, pulley, inclined plane, screw, wheel and axle (including gears), wedge
- Conceptual formulas of volume, pressure, acceleration, and force moment
3. Take BMCT Practice Tests
Your goal is to find preparation materials that include questions that follow the format and difficulty level of the Bennett test. Your ideal BMCT practice test will consist of 55 questions, have a time limit of 25 minutes, and contain questions in the same topics and level of difficulty of the actual Bennett mechanical test. Do not settle for less because if your practice tests are unlike the actual test, you might be caught off-guard on test day. No need to add weight to potential test anxiety. Practicing with test-level materials is an invaluable component of the preparation; it gets your mind accustomed to the difficulty and time-constraints of the test, relieves tension, and builds self-confidence on test day.
4. Find a Good Online Preparation Course
This is the online era, and preparation books or random PDF files tend to be obsolete. Nowadays, it is best to rely on online courses, which tend to get updated along with the test. When you choose your course, make sure that it offers practice materials that follow the specific format of the BMCT; otherwise, you might sharpen skills you do not need, and neglect those that you do. In addition, make sure to prepare with a course that follows the curriculum of the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test-ii, the current version of the test, and not the previous BMCT test versions.
5. Refine the problem by going “extreme”
Most of the Bennett test questions are based on a single mechanical or physical principle. While the differences between the answers may be subtle, you should take these differences to the “extreme” and to consider the situation in light of that. This sort of inspection usually makes the underlying principle more obvious and the question more solvable. It will also help you in memorizing and internalizing the knowledge gained by the solution.
For example, if a problem compares the power of one pulley versus two pulleys, consider it as one pulley versus many. If someone tries to lift a weight by a lever and you see two lengths of the lever arms, imagine the shorter one to be shorter, and the longer one longer.
Test Features
What are the differences between the BMCT and the BMCT-II?
There are some differences between the BMCT-II tests and the now-retired BMCT. The former is the newer version and is the only one still in use. The BMCT-II contains 55 questions and takes 25 minutes to complete, while the earlier BMCT contained 68 questions and took 30 minutes to complete.
Also, the old BMCT contained 18 categories of mechanical questions while the BMCT II contains only 12 categories (see table above).
Timed test
This multiple-choice test is timed, and you will have less than 30 seconds to complete each question. Therefore, it is essential to practice in advance and be ready to answer each question correctly as quickly as possible.

Question bank
In the BMCT-II, multi-level questions are randomly taken from a continually refreshed bank of items. The test questions vary in difficulty and do not necessarily get more challenging as they are answered. No two tests are the same, which is why the test can be taken without a proctor present.
Online and paper and pencil versions
The BMCT test is usually computerized, but employers have an option for pencil and paper tests as well.
Skills and abilities assessed
Mechanical comprehension is the ability to understand and apply basic mechanical and physical concepts, as well as the key principles underlying the workings, maintenance, and repair of machinery and equipment.
BMCT–II was developed to help identify individuals with good mechanical comprehension abilities and those with an aptitude to understand and apply mechanical concepts and principles to solve problems.
iPREP: Concise. Focused. What you need.
Sign up
Immediate access
Practice
Online self-paced
Pass
Ace that Test!
Technical Facts
Common Names of the Test
While the official name of the test is the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test II, the test has many unofficial names, including:
- Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test
- Bennett Mechanical Aptitude Test
- Bennett Test
- Bennett Mechanical Test
- BMCT
- BMCT Test
- Pearson Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test
Jobs and Positions That Require Passing the Bennett Mechanical Test
Many organizations and companies utilize the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test for screening purposes. If you pass the test, you will open yourself up to the following:
- A fulfilling career in a company such as Coca-Cola, Delta Airlines, Nestle, or Dupont.
- A job in the following areas:
| Group | Occupations |
|---|---|
| Installation/Maintenance/Repair | Facility maintenance, HVAC technician, equipment installation technician |
| Skilled Trades | Electrician, welder, plumber, carpenter |
| Machine Operator/Machinist | Machine operator, machinist |
| General Labor | Laborer, material mover/handler, groundskeeper |
| Vocational/Technical Student | Student in a vocational/technical program requiring mechanical comprehension |
| Mechanic | Automotive, motorcycle, diesel, aircraft |
| Engineer | Mechanical, electrical, civil, aerospace |
| Industrial/Technical Sales | Industrial product sales, technical product sales |
Level of Difficulty
On the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test II, each question is assigned a level of difficulty, ranging from simple to very difficult. Each test has a set number of questions at each difficulty level, ensuring that every candidate who takes the test faces the same number of simple, difficult, and very difficult questions. This allows administrators to compare scores despite the fact that each test uses different questions pulled from the question bank. All the while, all test takers still take the same number of questions per subject.
Full-color, updated test
The questions on the BMCT-II test are presented in color and reflect the 21st-century workplace.
Results Scale and Interpretations
How does the BMCT scoring work?
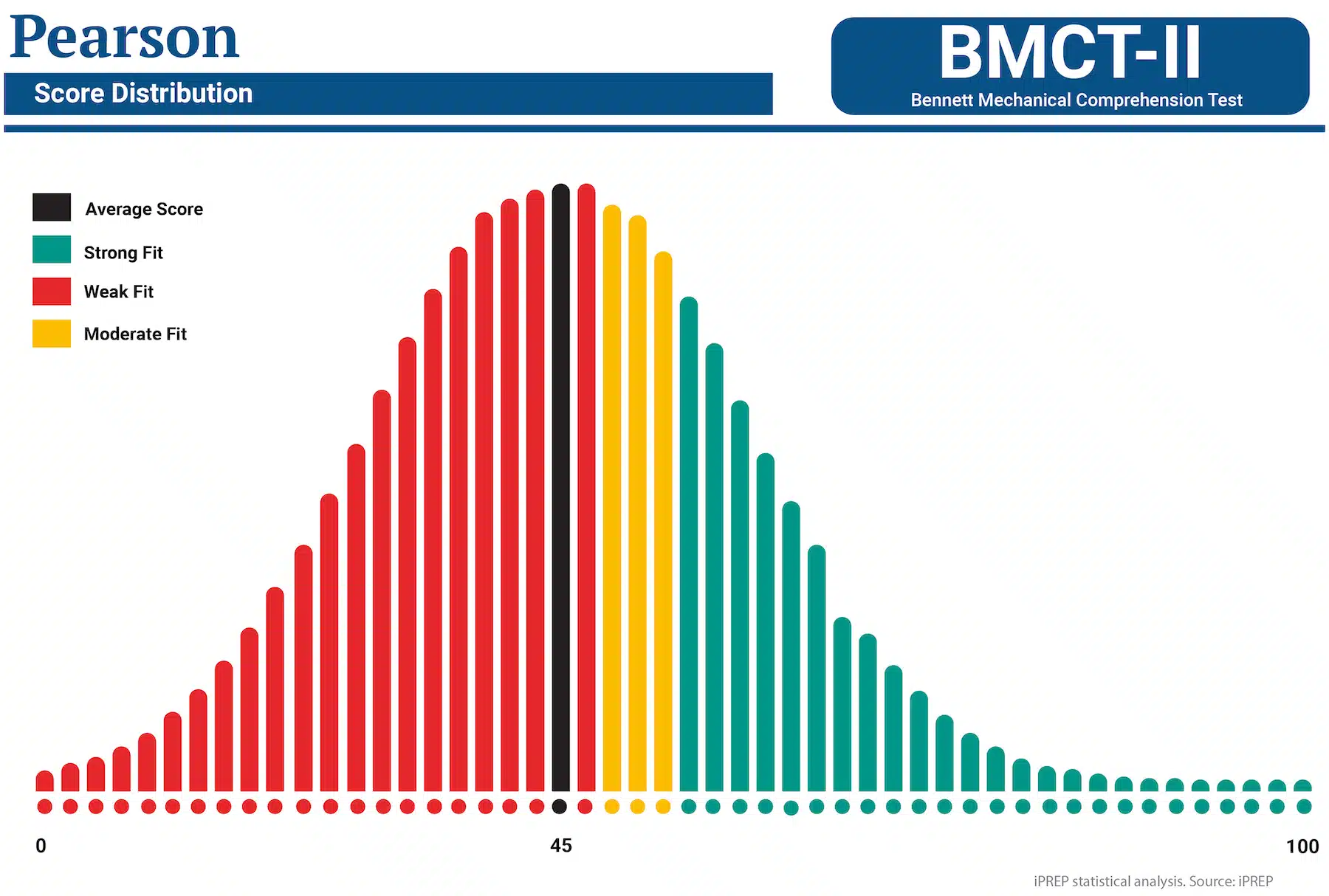
Since the questions vary in difficulty, you will not receive a raw score (number correct). Rather, you will see your percentile score, ranked among your peers.
The average (mean) score among Bennett test takers is 43-48, depending on the occupation. This means that in order to pass the BMCT, you must answer over 80% of the questions correctly (and aspire to 90-100% correct responses) to be chosen for a job. It is very important to try to score as high as you can so you can outrank the competition, which is why it is imperative to study in advance.
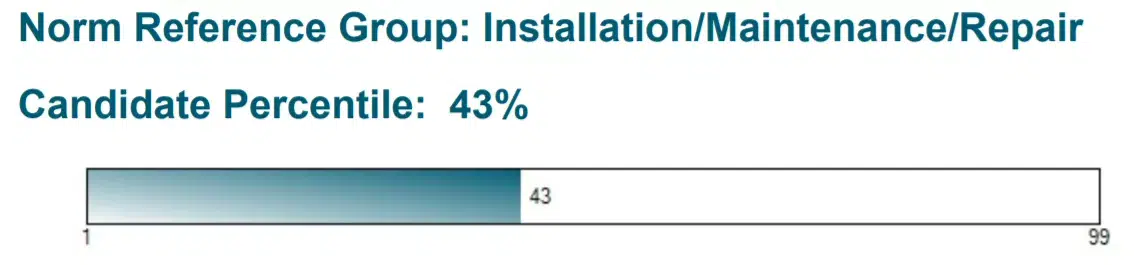
Description: John Sample’s score is higher than or equal to 43 percent of the Installation/Maintenance/Repair norm group.
What does your Bennett test score tell about you?
Your score will show potential employers and schools whether you are likely to succeed in a career that requires mechanical comprehension. Doing well demonstrates a proficiency in concepts and principles and indicates that you will be able to complete tasks that are assigned to you.


Interpreting Your BMCT Test Score
Your score will be presented in multiple formats, including as a percentile (see above). This will enable potential employers to compare your scores to those of past candidates in the database. Your Bennett mechanical aptitude test percentile score is not a raw score; it shows how you performed in comparison to other Bennett test takers.
You can use the following guideline to better understand your score:
Low scores up to 40 indicate that you don’t fully understand the principles involved, and it will take longer for you to learn the job and may require more supervision.
Mid scores up to 60 indicate that you have a solid understanding of the concepts, and you would be a good hire. High scores above 60 indicate that you have an excellent grasp of the concepts, you learn quickly, and you would be a very good hire.
BMCT FAQs
The Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test is one of the toughest, most respected mechanical tests being used today. It is used to screen potential employees and students.
The Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test is a 55-question test that you must complete within 25 minutes. It tests you on 12 categories of questions, including acoustics and optics, center of gravity, electricity, gears and belt drives, gravity and velocity, heat, hydraulics, pulleys and levers, resolution of forces, centrifugal force, inertia, shape and volume, structures, planes, and slopes.
We recommend that you have at least a basic command of mechanical principles underlying each of the test categories to be comfortable taking the exam. Practicing with iPrep will improve your scores and help you get ready for the test.
The best way to prepare for the Bennett Mechanical Test is to take online courses that cover the material and offer simulated test experiences so that you are prepared on test day.
The Bennett test has 55 multiple-choice questions, and takes up to 25 minutes to complete.
The Bennett test covers mechanical principles. If you are not familiar with them, you will need to spend a lot of time studying. For those who do know the material, the test is still challenging due to the short time frame you have to complete the test.
You will want to score an 80% or higher to be considered for employment.
BMCT-II stands for the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test – II. It is an updated version of the test.
The BMCT-II is a multiple choice test with 55 questions that must be completed in 25 minutes.
The Bennett Mechanical Aptitude test measures your ability to perceive and understand the relationship of physical forces and mechanical elements in real-world situations.
BMCT Test Tips
Read the following tips for help passing in the BMCT-II:
1. Work on your test-taking skills
Practice with iPrep so you can improve your skills and answer more questions correctly within the time limit. Practicing in advance will not only help you do better in a shorter amount of time, but help you feel more confident on test day.
2. Never leave a question unanswered
Each question in the Bennett test has three optional answers. One of these has to be the correct answer. That means you have a 33% chance to guess correctly even if you have no idea. If you are able to eliminate one of the answers, you increase your odds of being right to 50%. That’s a lot. If you leave a question unanswered, your chances of getting it right drop to 0%!
Since there is no penalty for wrong answers, the only reasonable thing to do is to answer each and every question, even if this means guessing or rushing through the last questions of the test.
3. Watch your time
Pay attention to the clock because a timed test has a limit. Don’t get too caught up on any one question. Taking timed practice tests will prepare you for the pressures of test day, and help you get used to answering quickly.
4. Get a good night’s sleep and eat breakfast
Resting well will help you concentrate on test day. Make sure you have already used the restroom and are ready to go when you start the test.
Eat a well-balanced meal before taking the test so you don’t get distracted.
5. Don’t forget your photo ID
If you arrive at the testing center without a photo ID, you will not be allowed to take the test. Double check that you have it before you leave the house.

Administration
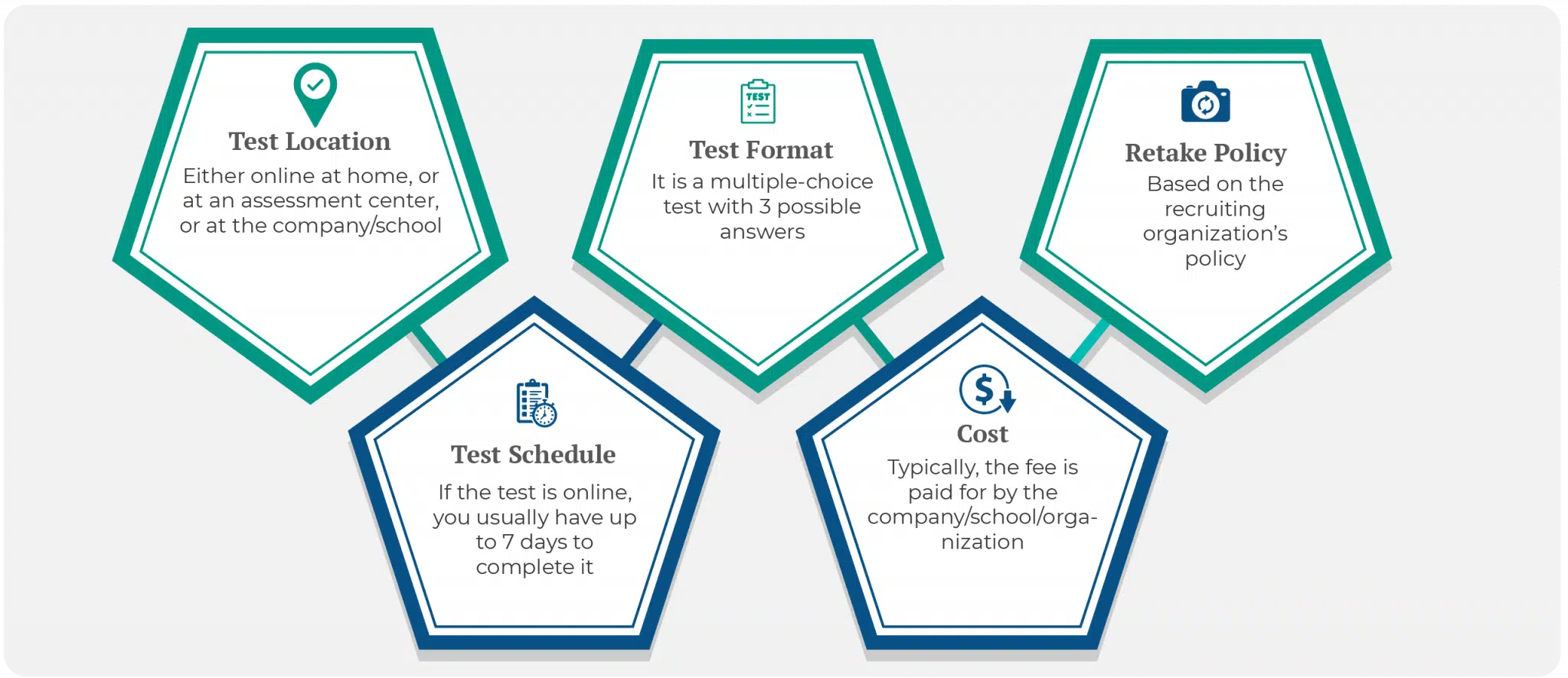
- Test Location: The BMCT is either sent as an invitation to take an online test at home or administered at a Pearson’s assessment center or at the company/school/organization.
- Test Schedule: The test is scheduled during the early stages of employment, usually right after sending in your resume. If the test is online, you usually have up to 7 days to complete it upon receiving the invitation.
- Test Format: It is a multiple-choice test with 3 possible answers. It is usually administered as a computerized test but can alternatively be a pen & paper test, especially if the recruiting organization schedules the test at its location.
- Cost: Typically, the applicant bears no financial responsibility as the BMCT fee is paid for by the company/school/organization requiring the test.
- Retake Policy: You may retake the test as many times as you’d like, restricted only by the recruiting organization’s policy.
Test Provider
The Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test (BMCT) and the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test II (BMCT-II) were created by Pearson Education/TalentLens. Manufacturers and other types of companies have been relying on Pearson to help assess potential candidates for mechanical/technical jobs for decades.
Information Sources
Disclaimer – All the information and prep materials on iPrep are genuine and were created for tutoring purposes. The Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test is a trademark and brand of NCS Pearson, inc. iPrep is not affiliated with Pearson, TalentLens, or any other company mentioned.
Free Bennett practice test: Get to know what the Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test II (BMCT-II) will be like by practicing with these sample questions:
Question 1 of 6

Which pulley mechanism reduces the effort of lifting a similar weight?
(If both reduce the effort, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is A.
In order to find the force required to lift the load, you need to determine the tension (W) in the string for both A and B—this can be seen in the image below.
For mechanism A, W =TA + TA; therefore TA = W/2
For mechanism A, W = TB, or TB = W
Now, the pulling force required to lift will be equal to the tension in the string that is holding the load. Tension is equally distributed between all pieces of the string pulling the load. Tension will decrease if you increase the number of strings pulling the load. In the given case, the tension in the string is W/2 for mechanism A and W for mechanism B. Hence, mechanism A reduces the required effort by half.

Question 2 of 6

While taking a right turn, which driver position is more likely to happen?
(If equal, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is B.
The car is taking a right turn, which means that it has a lateral component of velocity (v) in the right direction. This component governs the revolving motion of the car. When a body revolves around an axis, it faces centripetal force which is directed towards that axis. However, due to inertia, an opposite force acts on the body which is directed away from the central axis, known as centrifugal force. Because of this force, an object moving along a circular path tends to move outside the circle.
In the given case, the driver will also be pushed outside the circle by centrifugal force, as shown by position B.

Question 3 of 6

Which gunman’s bullet will strike the ground first?
(If at the same time, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is B.
From the given figure, gunman A is holding his gun upwards at an angle whereas gunman B is holding the gun completely horizontally. Suppose you extrapolate the trajectory of the bullet in the vertical direction (see the figure below). In that case, you can conclude that the bullet in case A will first move upwards due to its initial velocity. Then after some time, it will start moving downwards due to gravity and come to the level of its initial height, and only then fall down to the ground.
In the case of bullet B, it will not go upwards since the initial velocity is horizontal; instead, it will move directly downwards due to gravity.
Since only the downward acceleration is acting on the body (the gravitational acceleration “g”), bullet A will start moving downwards after reaching the highest point, while bullet B will move downwards from the beginning.
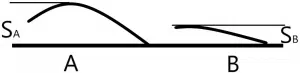
Question 4 of 6

The same load is being hung from each construct, which is made up of springs of the same length and stiffness. In which construct will the spring extensions be longer?
(If equal, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is A.
In both constructs, springs are placed in parallel. An in-parallel arrangement of springs increases their stiffness since the force extending the spring has to work against multiple spring forces. Therefore, the effective spring constant of the setup is increased.
If the spring constant of each given spring is “k,” then the equivalent spring constant is given as
kA = 2k and kB = 4k
Extension in the spring is given by Hooke’s law as:
Force (F) = Spring constant (k) * Extension (x)
For constant force, the extension of spring is inversely related to the spring constant. The extension in construct A will be double the extension of construct B since its spring constant is half that of B.
Question 5 of 6

Two water jets are ejected from tank pipes A and B. Which jet will reach farther?
(If equal, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is B.
You know that the hydrostatic pressure inside a tank filled with liquid is defined as P=ρgh, where ρ is the density of the liquid, g is the gravitational acceleration, and h is the depth of the point where pressure is being measured from the liquid level.
Now, in the case of pipe A, the pressure exerted at that point will be due to the water head (hA) above point A, which is relatively low, as can be seen in the image. For point B, the pressure will be due to the pressure head (hB) which is greater. Since hB>hA, the water jet B will shoot farther.
Did you know? – The Torricelli Theorem gives the speed of a water jet as v = √2gh

Question 6 of 6

Which mechanism would move the chain more slowly?
(If there is no difference, mark C.)
- A.
- B.
- C.
The correct answer is A.
You know that the tangential speed of meshed gears is the same. Also, the rotational speed and radius of gear are inversely related to constant tangential speed. In mechanism A, the driving gear (on the left) meshes with a larger gear. The smaller gear which moves the chain is connected to the same shaft as the larger gear, which means that the rotational speed of the smaller gear is equal to that of the larger gear.
However, in mechanism B, the driving gear directly meshes with the small gear, which drives the chain. This means that the smaller gear will rotate faster compared to the larger gear in mechanism A, which implies that the chain will move faster in mechanism B.
Sample Flashcards
Well done!
You have completed the Sample Questions section.
The complete iPREP course includes full test simulations with detailed explanations and study guides.
‘…TESTS THAT ACTUALLY HELP’

In the first 30 minutes of use I have learned so much more than skipping along the internet looking for free content. Don’t waste you time, pay and get tests that actually help.
Richard Rodgers
January 28, 2020 at 7:49 PM
About the course
Includes 4 full-length practice tests
Welcome to iPrep’s Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test (BMCT) Course.
This course will help you boost your skills and with it your confidence towards your upcoming BMCT exam. The course will provide you with the following tools and benefits:
- You will become familiar with the test’s various types of questions.
- You will be given a full-length BMCT-style simulation test. This simulation includes similar questions to those you will encounter in the real test with the same level of difficulty. It also has the same time limit as the real test. Experiencing the test’s time pressure will ensure it will not come as a surprise on test day.
- You will be provided with a great variety of helpful tips for the different types of questions. Some of the tips are in the introductory sections while most are in the detailed explanations that follow each question.
15
Learning hours
4
Practice tests
225
Questions
220
VIDEOS
By the end of this course, you will be more knowledgeable and comfortable with the BMCT Assessment – Knowledge and familiarity with the test are the two most significant factors that can help you maximize your score and improve your chances of success.
The course is comprised of both practice and learning sessions. In the following sections, we will guide you through learning lessons with essential information about your upcoming BMCT test. These lessons will review the basic skills and knowledge that are essential for succeeding in the test.
The course is then concluded by simulating full-length tests that accurately follow the structure and concepts of the BMCT. Once done, you will be able to get full question explanations and even see how well you performed in comparison with other people who have taken the test.
Wishing you an enjoyable learning experience!
Skills you will learn
Mechanical Comprehension
Simple Machines
Everyday Mechanics
Curriculum
- Course Introduction
- Mechanical Comprehension
- Simple Machines and Mechanical Advantage
- Understanding Fluid Mechanics
- Common Forces that Appear in Mechanical Tests
- Additional Mechanical Knowledge for Aptitude Tests
- Time Management Tips
- Full-Length BMCT-Style Test Simulations
- Course Conclusion
Customer Testimonial

Very good study guide and practice exams. I’ve worked as a civil engineering inspector for 20 years and I was surprised that my new potential employer asked me to take the Bennett Mechanical Test. I’m very glad I took this course because the practice questions really helped put my head back in the theoretical aspects of engineering. The answer explanations are thorough yet simple. I definitely recommend this course!
Paula Spencer
May 27, 2020 at 1:46 AM
Reviews

Sadio Adama K***
October 19, 2025 at 4:34 PM
I love iPrep lessons; they are very straightforward and easy to follow. The explanations and practice questions helped me understand the concepts quickly and build confidence for my test.

Leonel C********
October 6, 2025 at 6:07 PM
Acabo de adquirir este curso y estoy emocionado por presentar mi prueba, al parecer este es curso bastante completo y fácil de entender

Sean g***
September 24, 2025 at 12:19 AM
This is very helpful. The videos really break down the questions. Way easier then searching the web or watching videos as some questions I need to learn more about then others! 5 star

kalpesh p****
September 22, 2025 at 11:13 AM
need better picutres or signs to make it clear understanding of the situation or questions. need more tests to practice. details explaination in moving graphics will give better learning.

iPrep
September 23, 2025 at 7:30 AM
Thanks so much for your detailed feedback kalpesh. While we don’t have plans for moving animations or additional test simulations at this time, we’ll definitely keep your suggestions in mind. We’ll also take another look at the image clarity to make sure everything is as clear and helpful as it should be.

olivia g*****
September 14, 2025 at 7:22 PM
Lot of great useful information; wish the practice flaw cards were by category instead of random questions. Videos are a plus

Duncan H****
August 13, 2025 at 4:59 PM
iPrep was great in preparing me for the Bennett mechanical aptitude test. I would definitely reccommend it to anyone looking to boost their scores.

Kelly T*****
August 10, 2025 at 8:41 PM
Took the test first time and failed with a 55%. Bought the IPREP practice guide and passed with a 91%. If you are willing to take the time to study, learn and understand you will pass the test. This practice guide is very informative and explains the mechanics in depth to really help you understand.

Kelly T*****
July 29, 2025 at 10:09 AM
This course has given me all the building blocks I need to pass my test. It is very in depth and explains everything thoroughly to help you understand the fundamentals.

Bill J****
July 28, 2025 at 9:47 PM
I absolutely love the clarity and content of the videos on this prep course. Adding the written portion after watching the videos has been very helpful! Thank you!